This article explains GDPR – the General Data Protection Regulation, how it affects WordPress websites and how to achieve compliance for the law. The article provides a detailed guide about GDPR, its principles, and its rights and highlights the privacy measures implemented by WordPress to ensure compliance with GDPR.
Since European Union introduced the GDPR, a major shift has happened in the internet world. People became more concerned about their privacy, and governments all over the world introduced their own versions of GDPR.
These privacy laws are really important, especially when you have international clients or customers. Even slight negligence can cost you millions of euros as fines. Here is a list of the biggest GDPR fines so far.
GDPR, or General Data Protection Regulation, is a regulation passed by the European Union on May 25, 2018. It came into effect to protect citizens’ data privacy from companies both within and outside of Europe.
In simple terms, GDPR is a set of regulations that every business or data handler must adhere to when handling the personal data of EU inhabitants. GDPR has set a benchmark for privacy laws across the world.
As said in the introduction, countries all over the world are forming their own regulations against data breaches, but GDPR is by far the most stringent data privacy law in the world.
Residents of California have a similar law called CCPA – The California Consumer Privacy Act. Similarly, Brazil has its LGPD – Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais. All in an effort to ensure the data security of people living in those countries so as not to get exploited by companies.
Also Read: A Complete Guide to Cookie Law for Businesses
GDPR clearly specifies eight fundamental rights for data subjects. As per GDPR, a data subject refers to any individual who can be directly or indirectly identified using an identifier like a user name, email id, or other factors specific to a person’s physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural, or social identity.
Under Chapter 3 of GDPR, there are eight rights for data subjects.
Firstly, the right to be informed, which means the data subjects have the right to know what data is collected, who processes it, why it needs to be processed, and where and how it is processed.
Secondly, the right to access personal data collected by the data holders. This right allows data subjects to access the data collected by companies. Users should know who all have access to their data and for how long it will be stored.
Thirdly, GDPR grants data subjects the right to object to the collecting or processing of data for unnecessary purposes like marketing and promotions. Users can refuse to give consent or withdraw consent to collect personal data.
The right to erasure, also known as the right to be forgotten, gives users the right to have their personal data deleted if it is no longer necessary for the purpose it was intended. This means that users can request that their data be deleted from a company’s database or system.
Then, the right to rectification gives data subjects the right to edit their personal data and to ensure that the data collected is accurate and up-to-date.
The right to data portability grants users the right to receive their personal data in a structured, organized, and machine-readable format. This allows users to move, copy or transfer data from one source to another.
GDPR grants users the right to restrict the processing of personal data for certain circumstances like the data obtained being inaccurate, the processing being unlawful, or the data handler no longer needs the personal data for the purpose it was intended.
Finally, the right not to be subject to automated decision-making allows Individuals not to be subject to a decision based solely on automated processing, including profiling, that has legal or similarly significant effects.
The General Data Protection Regulation is based on seven key principles that organizations must adhere to when processing personal data. These principles are as follows:
- Personal data shall be processed lawfully, fairly, and transparently.
- Limit the purpose by only collecting personal data for legitimate and specific purposes.
- Only collect the minimum amount of data for the purpose it was intended for.
- Ensure the collected personal data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Personal data should not be kept for longer than is necessary for the purpose for which it is being processed.
- The data shall be processed in such a way that ensures its integrity and confidentiality.
- Take accountability for the data collected from the users.
Also Read: Five Years of GDPR: A Look Back at the Impact of the EU’s Data Protection Law
WordPress and GDPR Compliance
As an open-source content management system that powers 40% of websites on the internet, WordPress has taken some actions to make the core software compliant with GDPR. Let’s see the different privacy measures introduced by WordPress to be compliant with GDPR and other privacy laws.
1. Privacy Policy Generator
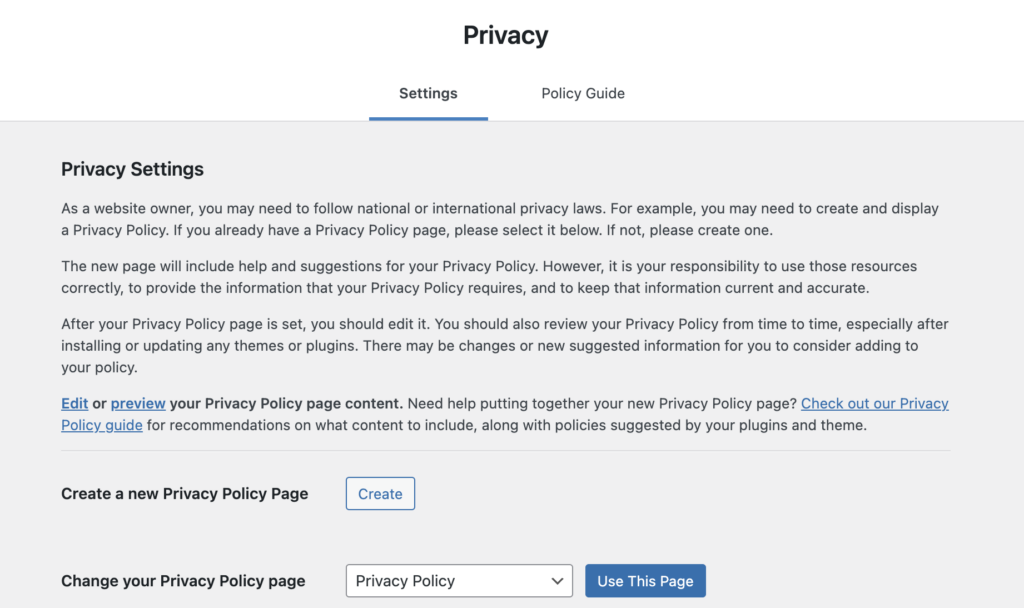
WordPress has introduced a privacy policy generator that helps website owners easily create a privacy policy page as required by GDPR.
You can go to Settings > Privacy from your WordPress admin page to access the privacy policy generator. Use the privacy policy template to create a privacy policy for your website. Make necessary changes to the privacy policy for your website and describe how and why data is collected on your website.
Privacy policies are to be taken really seriously as any breach or malpractice found could incur heavy penalties for websites. These fines could even destabilize small businesses if they aren’t careful enough with handling user data.
2. Erasing And Exporting Personal Data
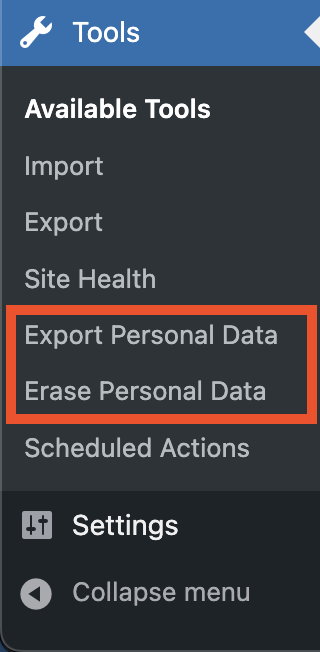
WordPress allows users to delete personal data stored on the website. Users can also export personal data from WordPress. These are based on the GDPR rights specifically the right to access and the right to erasure.
From Tools > Export Personal data and Tools > Erase Personal data, you can easily provide user information back to the customer or delete it entirely according to your customer’s request.
3. User Consent for Comments
Websites usually save user information while commenting just to reduce their effort in typing in their details every time they feel like commenting on any of the website’s forms.
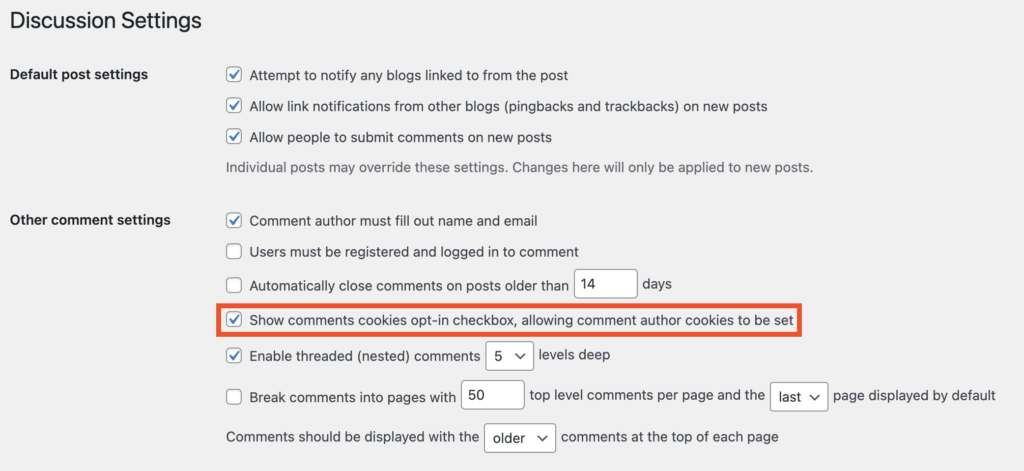
WordPress has an opt-in checkbox below the comments section that users can tick to give consent to personal data. This checkbox should also contain the reason why you are saving the information as well.
You can enable the opt-in checkbox from Settings > Discussion on the WordPress admin page.
To comply with GDPR you might need to take some serious actions on your website. We strongly recommend that you should hire a lawyer or ask for legal advice to help you comply with major privacy and security laws. A lawyer can provide you with the necessary information on making changes to your website from a legal perspective.
Analyze Data Collection on Your Website
Search your website for areas where customers may enter their personal information. Even their preference for products can also be considered personal data in this case. Once you’ve identified all of these, you must confirm that you’re asking the visitor for permission, as well as guiding them on how the data collected is processed.
Forms, comments, carts, analytics, and email marketing list are some of the most obvious areas that you might want to get compliant with. Another way your website collects information from users is through cookies. Check out this article to learn how to identify cookies your website installs on the browser.
Obtain Prior Consent From Users
After identifying the data collection process on your website, make sure to obtain prior consent from users for collecting their personal data. You can create a cookie consent banner on your website to obtain consent from users for loading cookies. The GDPR Cookie Consent Plugin by WebToffee will help you create and manage cookie consent on your website.
Also Read: Understanding WordPress Cookies
Update All Legal Documents
Keep your legal documents such as privacy policy and cookie policy up-to-date. Make necessary changes accordingly and ensure that users can access these documents on your website. Making legal documents for your website is better done with the help of a lawyer.
Check Out The Plugins On Your Website
It is important to ensure that the plugins, extensions, and themes you installed on your website should also comply with GDPR. Check out the plugin page in the WordPress plugin library or contact the plugin vendors to ensure that it is compliant with the GDPR standards and uninstall/update any plugins or extensions which haven’t already.
Allow Users to Access, Delete, or Modify Data
As per the 8 fundamental rights of GDPR, users have the right to access, delete or modify their personal data. So it is important to allow your website visitors to access their personal data stored on your website.
The core WordPress software provides the option to export and erase personal data. You can access the option from the Tools menu on the WordPress dashboard.
These are some important actions you can take to ensure GDPR compliance for your WordPress website. Is that all? Definitely not, that’s why we recommend you hire a legal person or seek legal advice from a lawyer. Apart from these, you should be well aware and up-to-date about the law and any changes made.
Roles of Plugins to Get You GDPR Compliant
There are a lot of helpful extensions and plugins to get you compliant with GDPR. Although individual plugins could be compliant in themselves, it doesn’t guarantee that your website will be compliant as well.
Thankfully, form builders, privacy policy generators, comment consent, and personal data export/erase features are all available through plugins.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, the WordPress core software version of 4.9.6 or higher is compliant with GDPR. But you should be aware that having the core software compliant with GDPR doesn’t make your website fully compliant with GDPR. You should make sure that all the plugins, extensions, themes, and any extra features added to the core website is also compliant as well.
Yes, you can use cookies on WordPress websites, but to comply with GDPR, you need to obtain explicit consent from users to process their data and provide them with options to manage their cookie preferences. You can create a GDPR compliant cookie banner for cookie compliance in WordPress.
Yes, you can, but you must ensure that these services and plugins also comply with GDPR and handle personal data in a lawful and secure manner.
A cookie policy is a document that explains how your website uses cookies, the types of cookies used, their purpose, and how users can manage their cookie preferences. You can use any policy generator tool or plugin to create a cookie policy.
Refer to this article to learn how to create a cookie policy: Requirements for a GDPR Compliant Cookie Policy
Conclusion
The complexity of our digital space will keep increasing at an exponential rate. Thus, it is important that we have strict laws that safeguard users from online threats of data breaches of every kind.
Like GDPR, nations across the world have started opening up to this challenge of data security. We’ll definitely see more regulations passed in this sense as data becomes a valuable commodity in the digital domain.
What are your thoughts on this article? Let us know in the comments.
Disclaimer: This article was intended for informational purposes only and does not represent legal advice. We have no intention of obtaining any kind of attorney-client relationship. If you are looking for legal advice we recommend you contact a professional.
We also recommend you read the below article:



