A subscription business model is a strategic setup where customers pay a recurring fee at regular intervals to access a product or service. This departure of businesses from traditional one-time transactions encourages an ongoing relationship between businesses and consumers.
In recent years, the subscription model has grown in popularity across diverse industries. From entertainment platforms to software services and even everyday essentials, companies are recognizing the value of offering subscription-based solutions. This shift is driven by the desire to establish long-term connections with customers, enhance predictability in revenue streams, and adapt to changing consumer preferences.
The rise of the subscription model shows that businesses are improving the way they connect with customers. This transformation happens in a world where convenience and flexibility are key factors.
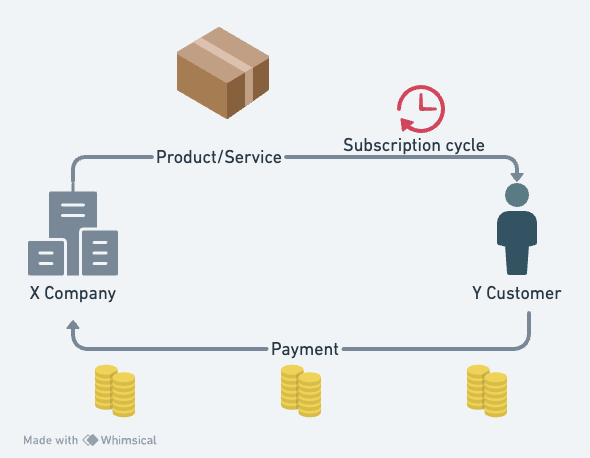
As the above diagram explains, a subscription business model works like a membership, where customers pay a regular fee, often monthly or annually, to access a product or service. When you subscribe, you typically gain continuous access to something valuable, like streaming services, online courses, or even regular deliveries of products.
The process usually involves signing up for a subscription, providing payment details, and then enjoying the benefits as long as you continue to pay the recurring fee.
For example, think of the streaming service Netflix. You subscribe by creating an account, entering your payment information, and choosing a plan. Once subscribed, you can watch a vast library of movies and shows as much as you want. The subscription fee is automatically deducted from your account each month, and as long as you pay, you retain access to the streaming content.
The recurring nature of subscription payments creates a stable income. With subscription models, businesses can forecast their earnings more accurately, making budgeting and financial planning a smoother process. This stability is especially crucial for startups and small businesses.
Beyond financial stability, these models can also give companies an idea of their behavior and preferences. This data can be analyzed to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and overall business direction.
Thus, by offering a continuous and smooth experience, businesses can develop lasting connections with their subscribers and cultivate long-term relationships with them. The ongoing value provided through regular access to products or services deepens the customer-brand relationship, increasing trust and familiarity.
This loyalty not only turns into sustained revenue but also boosts the chances of positive word-of-mouth referrals, creating an upright cycle of customer acquisition and retention. The subscription model thus becomes a two-way street, benefiting both businesses and their clients.
Subscription businesses come in various forms, catering to different needs and preferences. Here are a few types:
Subscription boxes or Product Subscriptions
This is the most common type, where customers subscribe to receive physical goods regularly. This type includes subscription boxes for beauty products, snacks, books, or even clothes.
Digital Subscription or Service Subscription:
Instead of receiving tangible products, customers subscribe to a service. This could be anything from streaming services like Netflix or Spotify to software-as-a-service (SaaS) models like Adobe Creative Cloud.
Access Subscription
Subscribers pay for exclusive access to certain features, content, or experiences. This model is often seen in online communities, premium content platforms, or even loyalty programs where members receive special perks.
Software Subscription
Here, the customers pay a regular fee to use any software. This is prevalent in cloud-based applications, where users subscribe instead of purchasing a one-time license.
There are different types of pricing models that can be applied to subscription-based businesses. Each pricing model has its advantages and is suitable for various business contexts. The key is to choose the one that matches the product or service offered and meets the needs of the target audience.
Freemium
Freemium is a strategic combination of free and premium offerings. Businesses provide a basic version of their product or service for free, allowing users to get a taste of what they offer. The goal is to convert free users into paying customers by showcasing the value of premium features. This model is popular for software, apps, and online platforms. Spotify app is an example.
Flat-rate pricing model
In the flat-rate pricing model, customers pay a fixed, regular fee for unlimited access to a product or service. This straightforward approach is common for subscription-based services like streaming platforms (e.g., Netflix). It reduces the need to worry about usage-based charges for customers.
Tiered pricing model
This model involves offering different packages or tiers at varying price points, each with a distinct set of features or levels of service. Customers can choose the tier that best fits their needs and budget. This approach is effective for a diverse customer base with different requirements. Zendesk can be considered an example, as it offers three different pricing plans.
Per-user pricing
In per-user pricing, the subscription cost is determined by the number of users or seats. This is common in business-oriented subscription services like project management tools or collaboration platforms. The more users a business has, the more they pay. Companies pay for the licenses they need, making it scalable for different-sized organizations. Canva is a best example of this.
Usage-based pricing
Some subscription models charge customers based on their actual usage of the service. This can be advantageous for businesses where usage varies among customers. For example, cloud services often use this model, charging based on the amount of data storage or bandwidth consumed.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on charging the cost of the subscription according to the perceived value it delivers to the customer. Businesses assess the value their service provides to customers and set prices accordingly. This model highlights the unique benefits and features of the product or service, allowing companies to charge a premium based on the value customers receive. If a service offers unique features or solves a critical problem for customers, the pricing may be higher.
Retaining customers is essential for subscription businesses. By consistently delivering value and fostering a positive relationship, companies can minimize churn and build a loyal customer base. Here are some key strategies to keep your customers.
Customer Engagement
Customer engagement is about keeping subscribers actively involved with the product or service. This often involves regular communication, updates, and creating a community around the brand. Subscription businesses use strategies like targeted email campaigns, in-app notifications, and social media engagement to keep their customers on track. By providing valuable and relevant content, subscription businesses can maintain a connection with users.
Personalized Experiences
Personalization plays a significant role in customer retention. Subscription businesses can make use of user data and preferences to create experiences. This could include personalized recommendations, customized interfaces, or exclusive content based on individual preferences. By making customers feel that the subscription is curated specifically for them, businesses enhance the overall value and make it harder for customers to switch to alternatives.
Customer Support
Responsive and effective customer support is a mainstay of customer retention. Subscription businesses invest in providing timely assistance, resolving issues on time, and ensuring a positive customer service experience. This can involve various channels, such as live chat, email support, or even phone support. A smooth and helpful support system builds trust and satisfaction, reducing the likelihood of customers churning.
Loyalty Programs
Implementing loyalty programs is a common strategy for retaining subscribers. Offering rewards, discounts, or exclusive perks to long-term customers encourages them to stay committed to the subscription. Loyalty programs also create a sense of appreciation, making customers feel valued and more likely to continue their subscriptions.
Feedback and Improvement
Subscription businesses actively seek customer feedback to understand their needs, preferences, and pain points. Regularly collecting and analyzing customer input helps companies identify areas for improvement. By demonstrating a commitment to enhancing their service based on customer feedback, businesses show that they value their subscribers’ opinions and are dedicated to providing a high-quality experience.
Incentives for Long-Term Subscriptions
Many subscription models offer discounts or special incentives for customers who commit to longer subscription periods. This strategy not only provides a financial benefit for the customer but also reduces the likelihood of them canceling in the short term. It aligns with the mutual interest of both the business and the subscriber for a stable, long-term relationship.
Technologies and platforms will contribute to the efficiency, effectiveness, and success of subscription-based businesses. Here are some significant technologies and platforms to be considered for subscription models.
Billing Systems
Billing systems automate the process of invoicing and collecting payments from subscribers. They ensure accuracy, reliability, and security in handling financial transactions. Advanced billing systems can support various pricing models, including tiered pricing, usage-based pricing, and personalized discounts. Automation reduces the risk of errors and streamlines the billing process, contributing to a smoother customer experience.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM tools help businesses manage customer interactions, track customer data, and improve relationships. In the context of subscription businesses, CRM systems enable personalized communication, customer segmentation, and targeted marketing efforts based on individual preferences and behaviors.This, in turn, contributes to customer retention and loyalty.
Analytics Tools
These tools provide insights into subscriber behavior, usage patterns, and key performance indicators. By interpreting this data, businesses can make informed decisions to improve their subscription offerings. Analytics also help in identifying trends, understanding the effectiveness of marketing strategies, and optimizing pricing models for better profitability.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
For businesses that deliver digital content or services, a strong CMS is essential. It enables efficient content creation, management, and delivery, ensuring that subscribers have access to the latest and most relevant content.
Payment Gateways
Smooth and secure payment processing is important for subscription businesses. Payment gateways facilitate transactions, handle recurring payments, and ensure the security of financial information.
Customer Support Tools
Efficient customer support tools, such as ticketing systems and chatbots, enhance the customer experience. They provide quick responses to inquiries, troubleshoot issues, and contribute to overall customer satisfaction.
Security Measures
Given the sensitive nature of financial and personal data in subscription models, ensuring security and compliance is important. This includes secure payment gateways, encryption protocols, and authentication mechanisms to safeguard customer data. Ensuring the security of transactions builds trust with subscribers and protects the reputation of the subscription business.
Automation and AI
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies make various aspects of subscription management easy and simple. Automated customer onboarding, personalized content recommendations, and AI-driven customer support enhance efficiency and the user experience. AI algorithms can also predict customer behavior, helping businesses proactively address potential issues and reduce churn.
Covering the legal and ethical aspects is important for subscription businesses to build trust with customers and maintain a positive reputation. Here are key considerations:
Subscription Terms and Conditions
Clear and transparent subscription terms and conditions are essential. Businesses must outline the terms of the subscription, including pricing details, renewal policies, and any potential changes to the service. Compliance with consumer protection laws is paramount to avoid legal issues and maintain ethical business practices.
Privacy Concerns
Subscription businesses often collect and handle sensitive customer data. Following data protection laws and implementing strong privacy policies is non-negotiable. Clearly communicate how customer data will be used, stored, and protected. Obtaining consent for data collection and giving customers control over their preferences demonstrates respect for privacy rights.
Renewal Practices
Subscription renewal practices should be transparent and fair. Clearly communicate renewal dates, pricing changes, and cancellation procedures. Auto-renewal mechanisms should be clearly disclosed, and customers should have the option to opt out easily. Ensuring that customers are informed and have control over their subscription status contributes to a positive customer experience and helps avoid legal issues related to misleading practices.
Refund/Cancellation Policy
Have a well-defined refund and cancellation policy. Clearly explain the terms and conditions related to refunds, including under what circumstances they are applicable and the procedures for requesting them. Make sure the refund/cancellation policy aligns with consumer protection laws to avoid legal complications.
Compliance with Local and International Laws
Subscription businesses operate in various jurisdictions, each with its own set of laws and regulations. Adhering to both local and international laws is crucial to avoid legal complications. This includes compliance with consumer protection laws, data protection regulations, and any industry-specific regulations that may apply.
Conclusion
By offering value through recurring services, businesses can foster long-term customer relationships while ensuring a steady revenue stream.
Starting a subscription business demands a strategic combination of planning, ethics, and customer focus. From market research to transparent pricing, engaging content, and legal compliance, the journey involves navigating various aspects.



