This article explains in detail the impact of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) on Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager. In this article, you will learn why you should care about GDPR and how to ensure Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager comply with GDPR.
Ever since General Data Privacy Regulation (GDPR) came into effect on May 25th, 2018, most Internet services have been struggling to get into GDPR compliance with the new standards, and Google is no exception here. Although the company has made some big changes, there is still some confusion regarding GDPR Compliance for Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager.
In October 2020, Google introduced Google Analytics 4 with the goal of creating a safe and sustainable platform for data processing. Does Google Analytics 4 comply with GDPR?
Dive in, and we will discuss this in this article.
Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics 4 (GTM & GA4)
Google Tag Manager is a free tool offered by Google to allow website owners to add tags on their website to track user interactions like the number of clicks, video view counts, etc.
Tags are code snippets based on Javascript, HTML, or CSS. GTM supports various tags, including custom HTML tags, image tags, etc. Website owners use tags to track and analyze user behavior and enable third-party website tools.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the latest version of Google Analytics, an analytics service offered by Google to track user behavior on the website. GA4 has advanced analytics features and is more privacy-focused than its earlier versions. I won’t trouble you with the complexities of GA4, which is a topic for another day. If you need additional information, refer to this guide.
Privacy Concerns Related to Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager
As we have discussed above, Google is trying to make its analytical service more privacy-focused. Still, there are quite a few challenges and concerns. Let’s see in detail what they are.
- Collection of personal data: As you may know, Google collects personal data for analytical and advertising purposes. This data, such as IP Address, Cookie ID, etc., can be regarded as Personally Identifiable Information and are subject to GDPR guidelines.
- Lack of transparency: Website visitors are not fully aware of what data is being collected and how they are being processed. This can cause serious compliance issues with major privacy laws.
- Limited control for website owners: Google Analytics provides website owners with limited control over how data is collected and used. While it is possible to configure certain settings, such as IP anonymization, some data will always be collected by default.
- Limited control for site visitors: Website v have limited control over the data that is collected by Google Analytics. Although there are some browser extensions and tools to opt out of data collection, it is not always easy to do so.
- Potential for data breaches: Google Analytics is not immune from data breaches and is always at risk of a data breach. It is possible that sensitive personal data could be exposed, putting individuals at risk of identity theft and other types of fraud.
Impact of GDPR on Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager
GDPR is considered a vital step towards protecting the fundamental rights of privacy of users. It provides the users with the right to data portability, the right to data access, and the right to be forgotten. GDPR not just provides the user with user consent but also asks the website to save the same as evidence for any future reference needed.
Even in the case of loss of data or breach of data, the policy affirms there is an immediate notification sent to data protection authorities as well as the users. If your organization does not compile the rules of GDPR, a penalty of €20 million or 4% of worldwide revenue is applicable.
You may now be aware that GTM and GA are utilized for tracking user behavior and processing user data, which can potentially create compliance issues with GDPR regulations. Let’s go through different ways the GDPR will affect GTM and GA.
- Obtain explicit consent: GDPR clearly states that website owners should obtain explicit consent from the users before processing their data. This is applicable for the data tracking by GTM and GA. Website owners should inform users about how their data is being used and give an opt-out option.
- Transparency in data processing: Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics use various user data to identify user behavior on a website. As per GDPR guidelines, site owners should state the purpose of data collection and should only use the data for the stated purpose.
- Limit data retention: Once the purpose for collecting data is fulfilled, it should not be retained or utilized any further.
- Secure the user data: Website owners should take appropriate security measures to ensure user data is safe and secure on their websites. Also, users should be informed in case of a data breach.
Now that was about GDPR and how it affects all websites. Google, too has constantly been updating its policies to match the rules of GDPR.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, Google Tag Manager (GTM) is GDPR compliant. However, the tags and pixels added to GTM by the website owner may collect site visitors’ personal data and may not be compliant with GDPR. Website owners are responsible for ensuring compliance with the tags used in the websites.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) are data elements used to identify an individual’s identity. Name, Mobile Number, and IP Address are some examples of personally identifiable information.
No, you cannot use Google Analytics without consent from users if you are processing the personal data of European Union (EU) citizens. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires that you obtain the explicit consent of individuals before collecting and processing their personal data.
Data residency refers to the physical location or region where data is stored and processed. Companies and organizations that collect and process personal data need to take this into consideration since it could affect compliance with data protection and privacy regulations.
No. Google Analytics, by default, is not GDPR compliant. However, the GA4 has implemented a lot of privacy enhancing features that will help you comply with GDPR.
How to Ensure GDPR Compliance for Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager?
Google Analytics is a tool that allows you to get real-time insights into how a website is being used, when, and by whom. It works by means of a tracking code that is added to pages of your website. Each user is given a unique ID to recognize them when they return to the website.
Google Tag Manager is another tool that allows placing pixels that can drop third-party cookies, which allows tracking the performance of promoted posts or double-click conversion tags.
The functions of both tools are against GDPR rules as it states that the visitor’s prior consent must be taken before assigning cookies that track them or collect their data. The following steps can be taken to make sure you are using both tools as per GDPR terms:
1. Auditing Data
Auditing all the data collected is a good step to start, as no personal information should be shared or transmitted without the consent and knowledge of the user. Filtering out personal data is not enough; it needs to be made sure that no data is sent to Google Analytics in the first place.
Collecting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is against the terms of service of GA. Audit the data collection process on your website and ensure that you are not processing PII.
You can access the data collection details from the Data settings of GA4.
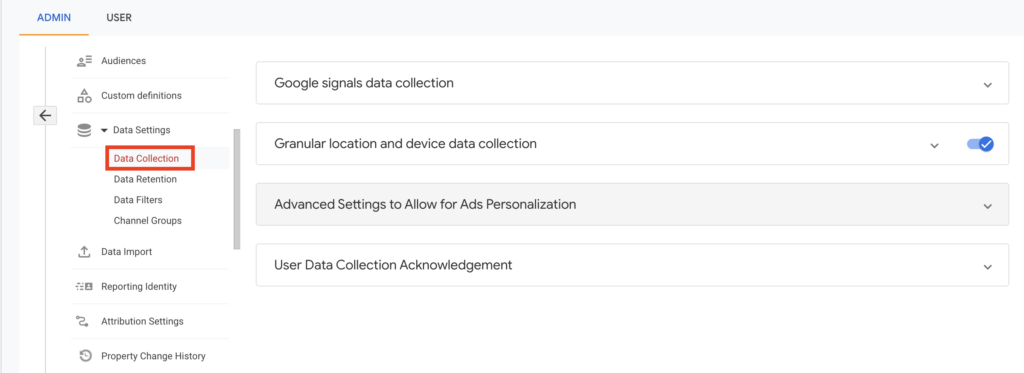
Here are some recommendations by Google to avoid sending PII:
- Remove personally identifiable information (PII) from user-entered data.
- Avoid the use of precise location data.
- Ensure that page URLs do not contain PII.
2. Anonymizing IP
IP addresses are considered personally identifiable information, so anonymizing IP is important as IP addresses may not be shared, but Google uses them to get geolocation data. You can turn on the IP Anonymization feature of Google Analytics using Google Tag Manager.
Go to Fields to set and add a new field named ‘anonymizeip’ and make its value ‘True’. This will serve the same purpose as IP anonymization.
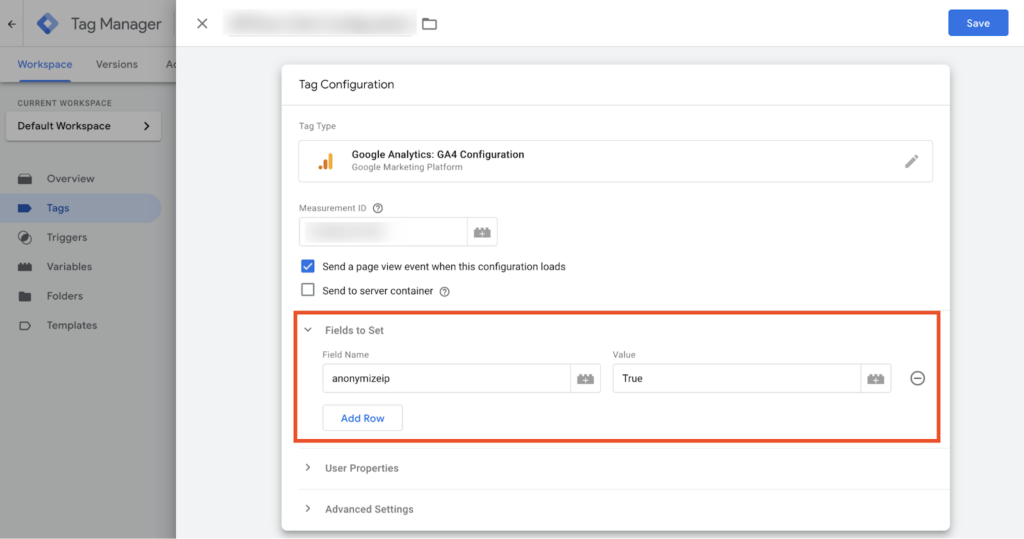
The result of making this change is that Google will promptly anonymize the IP address by removing the final octet of the IP address, which results in your IP being represented as 123.123.123.0, with the last portion/octet replaced with a ‘0.
While there may be a slight decrease in the accuracy of geographic reporting, anonymizing IP can help reduce non-compliance risks. This option, once implemented, will make the end portion of your IP zero, thus preventing Google from tracking your location.
Also Read: What is Google Consent Mode?
3. Identify the Collection of Pseudonymous Identifiers
Pseudonymous identifiers are data elements used to identify users without revealing their personal identity. These elements are associated with temporary identifiers instead of their name or other personal information. User IDs, email addresses, and transaction IDs are the most common pseudonymous identifiers used by Google Analytics.
These are mostly alphanumeric database identifiers. Collecting pseudonymous identifiers does not risk your compliance with GDPR or Google Analytics Terms of Service. But you have to obtain explicit consent from users and mention this in your privacy policy with relevant information like what data is collected and how it is used.
You can also give users the option to raise data deletion requests for Google Analytics. Refer to this article for more information.
4. Updating Legal Policy Documents
The data processing on the website should be clearly stated in the privacy policy of your website. Clear instructions need to be given to the users for opting in and out of data being collected in plain and simple language. The privacy policies must always be specific and up-to-date for Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager.
A privacy policy should contain relevant information like:
- What data is being collected?
- Who collects it?
- How is the data being collected?
- What is the purpose of collecting this data?
- How will the data be utilized?
- Who has access to this data?
- What impact will this have on the individuals whose data is collected?
- Is it possible that the intended use may result in objections or complaints from individuals?
Refer to this article to learn more about creating a privacy policy for WordPress websites.
It is also recommended that you have a detailed cookie policy document as per GDPR guidelines.
5. Provide an Opt-in / Opt-out option
If you are using Google Analytics to collect UserID or hashed Personally Identifiable Information to assist in user behavior profiling or for any other advertising purposes, you have to provide an opt-in consent mechanism and the option to opt-out at any time.
You may need to provide the opt-in consent for all EU visitors to your site since Google Analytics also records an online/cookie identifier known as the GA Client ID. GDPR specifically mentions that online identifiers are considered personal data and thus would be subject to this regulation. You may also seek legal advice at this point for more information.
For providing an opt-in/ opt-out option and displaying a disclosure of using analytical cookies, you can use a cookie banner on your website. A cookie banner is a notice on your website stating that you use cookies and have buttons to obtain consent from site visitors to load cookies. GDPR requires you to state the function and purpose of cookies and provide a link to your website’s cookie policy and privacy policy.
If your website is built on WordPress, check out the WordPress GDPR cookie plugin from below to create cookie consent banners for your website.
6. Provide data deletion for users
Users have the right to have their data deleted from the database upon request. GA4 has some advanced data deletion options that allow you to delete user data.
Below are the available data deletion options in GA4:
- Limit Data Retention
- Schedule Data Deletion
- Opt-Out of Data Sharing
Now, let us see how to enable each option:
1. Limit Data Retention
Google Analytics 4 allows you to limit the data retention period for your website. This is clearly stated in the eight principles of GDPR. When the original purpose of user data has been achieved, the data should no longer be kept.
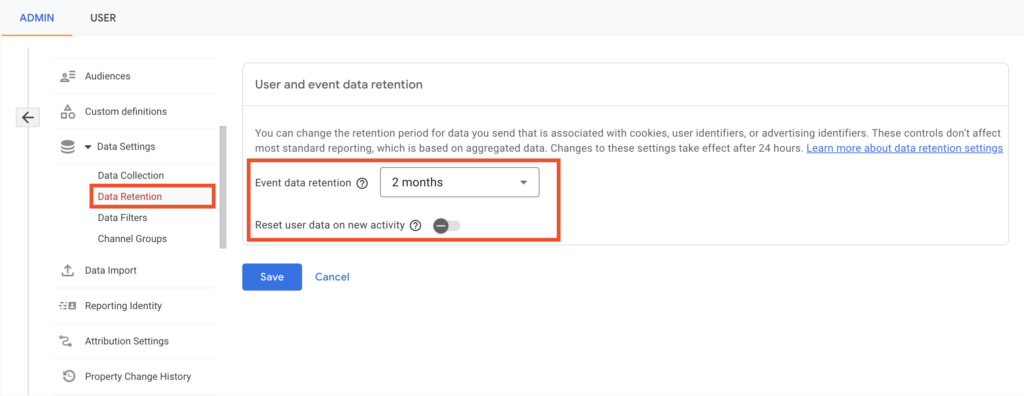
To limit the data retention on GA4:
- Go to the Admin page of your GA4 property
- Below the Property section, choose Data settings
- Select Data Retention from the dropdown.
- Now, choose a data retention period. GA4 offers data retention for 2 Months, 14 Months, 26 Months, and Unlimited. You can choose a period based on your requirements.
- Then, disable the Reset user data on new activity option so that user data will be deleted automatically after the set period and will not reset after each visit.
- Click on the Save button to save the settings.
2. Schedule Data Deletion
You can schedule data deletion requests in GA4 based on various requirements.
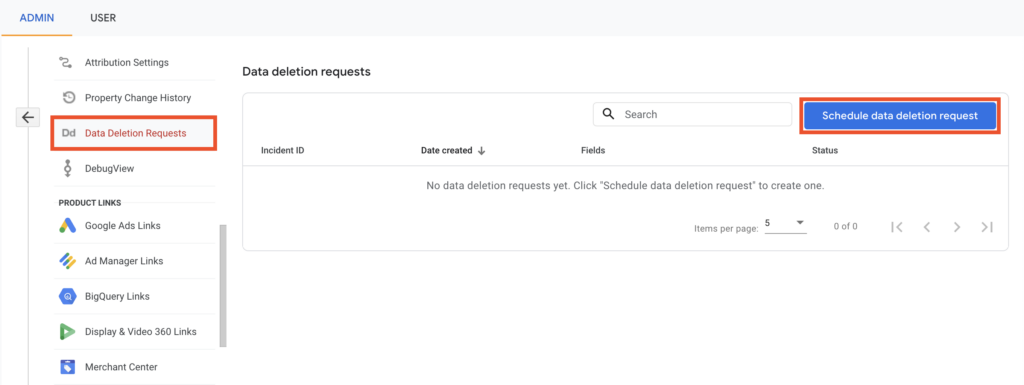
To access the data deletion configurations:
- Go to Data Deletion Request under the Property panel of the Admin page.
- Select the Schedule Data deletion request option.
- Choose a deletion type from the dropdown menu, and choose a date period for the data to be deleted.
- Click on the Schedule request button to schedule the request.
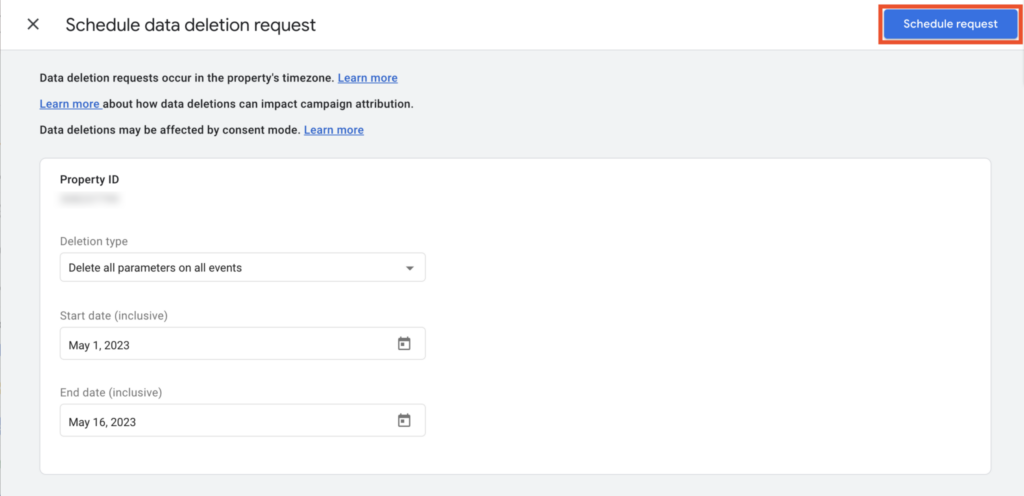
After scheduling the deletion request, you can cancel the request within 7 days.
3. Opt-out of data sharing
Google Analytics allows you to opt out of sharing the data of your website visitors with third-party services. To opt out of data sharing:
- Select the Data Sharing option under the Property panel of your Admin page.
- In Data sharing settings, uncheck the boxes next to services you do not want to share data with.
- Click on Save to save the changes.
These are the available options Google Analytics offers to delete user data.
Conclusion
GDPR regulations have put Google and its analytical and advertising services under strict scrutiny. While Google is making an effort to align its policies with GDPR guidelines, there is still much to do to achieve compliance. This article has provided valuable insights into how GDPR affects Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager and the necessary steps to ensure compliance.
By following the guidelines discussed in this article, website owners and businesses can take the necessary measures to protect the personal data of their users and avoid any potential compliance risks. If you have any further questions or concerns, please feel free to ask in the comments section below. Thank you for taking the time to read this article.



