Privacy by design is the concept that embodies the idea of being preventive rather than looking for a cure after being infected. In this article, we will be discussing the principles and significance of Privacy by Design.
In our data-driven world, where countless data exchanges occur daily, safeguarding data privacy has become increasingly challenging. That’s precisely why we need an approach prioritizing data privacy right from the start. This approach is known as Privacy by Design.
If you’re a business owner seeking to delve deeper into Privacy by Design and eager to implement this framework for your business, then you are in the right place.
Having said that, let’s get started.
Privacy by Design (PbD) is an approach that proactively integrates data privacy principles right from the design stage itself. From design through development to deployment, privacy is considered at every stage of product development.
It aims to embed privacy as an essential component rather than an afterthought or retrofitting measure.
The concept of Privacy by Design was first introduced by Dr. Ann Cavoukian, the former Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario, Canada. It has since gained recognition and adoption globally as a best practice for addressing privacy concerns in an increasingly data-driven and interconnected world.
Privacy by design is an approach as well as a framework. It helps businesses build better solutions that ensure their customers’ data privacy. Also, many data protection laws, such as GDPR, require you to comply with the PbD framework.
The Privacy by Design framework is based on a set of principles that helps you adopt a privacy-first approach throughout your design and development process.
Here are the core principles of Privacy by Design:
1. Proactive, not reactive; preventive, not remedial
Privacy should be considered from the beginning stage of a product lifecycle. Incorporating privacy right from the beginning stage will help you anticipate and prevent any privacy risks before they occur. By the time your product reaches the end user, it will be foolproof and privacy ready.
2. Privacy as the Default Setting:
Privacy should be kept as the default setting for your product. This means explicit consent is required from a user for collecting and processing personal data. The proactive approach while developing a product will help you make privacy the default setting for your product.
3. Privacy embedded into design:
Privacy considerations should be incorporated into the design process of systems, products, or services right from the beginning rather than being added as an afterthought. By embedding privacy into design, organizations, and designers take proactive steps to identify and mitigate potential privacy risks, implement privacy-enhancing features, and ensure that individuals’ personal information is handled with care and respect.
4. Full functionality – positive-sum, not zero-sum:
Privacy considerations should not hinder users from accessing a product’s essential features and usability. This means you can’t force users to consent to access a function. Privacy should be given as a win-win, not as a zero-sum option.
5. End-to-end security – full lifecycle protection:
User data should be protected throughout the lifecycle of the data. Robust security measures should be taken to prevent any data breaches. This principle ensures that user data remains protected from the moment it is collected until it is no longer necessary, maintaining the privacy and trust of individuals whose data is being processed.
6. Visibility and transparency – keep it open:
Businesses should take responsibility for how they handle personal information. They should use the data only for clearly stated purposes, and all relevant parties should be aware of those purposes. Ensure that they have comprehensive policies and procedures and make them easily accessible for everyone.
7. Respect for user privacy – keep it user-centric:
Last but certainly not least lies the core principle that underpins all others: Respect for user privacy. Businesses should Respect the privacy of their users. This motivates them to follow the actual concept of privacy by design. User privacy will be considered at every stage of a product lifecycle. This helps businesses to make better decisions in the product development process.
Also Read:
Why Should You Adopt a Privacy First Approach to Your Business?
Privacy Policy Template: How to Create a Well-Defined Privacy Policy for Your Website?
General Data Protection Regulation is the first law that mandatorily requires you to follow the Privacy by Design framework. The principles of Privacy by Design align with that of the GDPR. There are clear citations from GDPR about the concept of Privacy by Design.
“The controller shall implement appropriate technical and organizational measures for ensuring that, by default, only personal data which are necessary for each specific purpose of the processing are processed.”
Reference: GDPR Article 25
GDPR requires organizations to implement measures such as data minimization, purpose limitation, transparency, security, and user consent, which are fundamental components of Privacy by Design. Organizations are expected to assess and address potential privacy risks, adopt privacy-enhancing technologies, and ensure that privacy is embedded into their data processing activities.
Privacy by Default
Privacy by Default itself is a principle of the Privacy by Design framework. According to this principle, any default settings or configurations within the application should prioritize privacy as a primary consideration.
When privacy is set as the default, it means that personal information is automatically protected without individuals having to adjust settings or opt-in for privacy features manually. Privacy-friendly defaults may include features like limited data collection, strict access controls, and strong encryption.
By implementing Privacy by Default, organizations prioritize their users’ privacy from the outset, making it easier for individuals to maintain control over their personal information. It helps to safeguard privacy without burdening users to take extra actions to protect themselves.
Also Read: eCommerce and Digital Privacy – A Comprehensive Guide
The process of implementing the Privacy by Design framework will vary depending on your business. However, the concept integrates privacy considerations into your processes, systems, and practices from the beginning.
Here are some checklists to help you implement PbD for your business:
- Respect the privacy of your users:
The first and foremost thing you should do is respect your users’ privacy. It gives you a reason why you should implement the Privacy by Design framework. It should not be the laws or fines for non-compliance that are the reason why you are implementing the PbD for your business. Respect the privacy of your users and take the necessary steps to ensure that users’ privacy is protected.
- Conduct a data assessment:
Conduct a comprehensive privacy assessment to understand the personal data you collect, process, and store, along with associated privacy risks. Identify areas where privacy measures need to be enhanced.
- Minimise data collection:
Adopt a data minimum approach for collecting personal information. The less data you collect, the less effort you need to safeguard user privacy. Use anonymous data identifiers wherever possible. You don’t always need the personally identifiable information of your users, so give users the option to provide alias names and anonymize IP.
- Develop privacy policies and procedures:
Create clear and accessible privacy policies that outline how you handle personal data, including purposes, data retention, security measures, and user rights. Develop procedures to ensure compliance with privacy policies.
- Implement security measures:
Data privacy without security is impossible, so it is important to Integrate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data throughout its lifecycle. This includes encryption, access controls, regular security updates, and staff training on data protection.
- Obtain explicit consent:
Obtain prior consent from users before collecting or using their personal data. Be aware of collecting explicit consent at every checkpoint you collect personal data from users. This includes cookie banners, login forms, opt-ins for newsletters, etc.
- Provide user control:
Give individuals control over their personal data by providing options to access, correct, or delete their information. Enable users to manage their privacy preferences and opt out of certain data processing activities.
- Embed privacy into system design:
Consider privacy during the design phase of new products, services, or systems. Incorporate privacy features like privacy settings, anonymization techniques, and privacy-enhancing technologies.
- Conduct Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs):
Perform PIAs to identify and mitigate privacy risks associated with new projects, products, or data processing activities. Use the results to implement necessary privacy controls.
- Foster a privacy-aware culture:
Train employees on privacy best practices and their responsibilities regarding data protection. Encourage a culture that values privacy and emphasizes the importance of privacy-conscious decisions.
- Regularly monitor and review:
Continuously monitor and assess your privacy practices to ensure ongoing compliance with privacy regulations. Stay informed about emerging privacy trends and update your privacy measures accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) are assessments conducted to evaluate the potential impact of a project, system, or process on individuals’ privacy. In simple terms, it’s a way to understand and address any privacy risks or concerns that may arise.
During a Privacy Impact Assessment, experts examine how personal information is collected, used, stored, shared, and disposed of. They analyze potential privacy risks and assess the effectiveness of existing privacy safeguards. The goal is to identify any privacy vulnerabilities and find ways to minimize or eliminate them.
Privacy by Design is a distinctive approach that incorporates privacy considerations from the initial stages of development. It sets itself apart from traditional privacy approaches, which often treat privacy as an afterthought or a retrofitting measure.
In contrast, Privacy by Design emphasizes the need for privacy to be integrated into every product development phase, ensuring that privacy becomes an inherent and ongoing concern throughout the entire process.
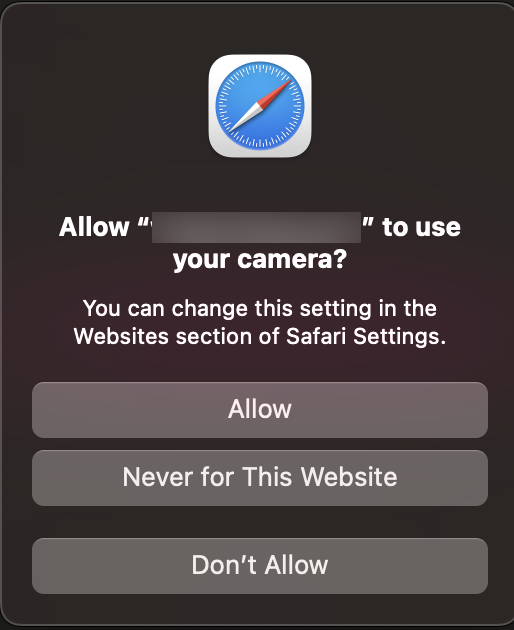
The Safari web browser is a great example of the PbD framework. It blocks trackers from processing your browsing history. You can block all the cookies and enable warnings for fraudulent websites. The browser will ask for explicit permission each time before accessing the camera, microphone, or location data.
These privacy-enhancing features are not limited to private browsing mode; they are automatically enabled for regular browsing, ensuring privacy by default.
Ensuring data privacy at every stage of product development can be daunting. That’s where automation tools and Consent Management Platforms (CMPs) come into play.
CMPs simplify the process of obtaining and managing user consent for collecting personal data. These platforms feature automated tools that streamline the creation of privacy policies and the display of cookie notices, among other functionalities. Businesses can significantly reduce the administrative burden associated with data privacy management by leveraging automation.
We have an automated cookie consent solution specifically designed for WordPress. Simplify your compliance efforts and ensure a seamless user experience.
Check out below for more information:
Disclaimer: This article was intended for informational purposes only and does not represent legal advice. We have no intention of obtaining any kind of attorney-client relationship. If you are looking for legal advice, we recommend you contact a professional.