We all are aware that the world of eCommerce is running on user data. It is the lifeblood of eCommerce websites. User data is very much essential for the functioning of an eCommerce store. From offering personalized suggestions to users and saving their payment information, shipping address, and a lot, eCommerce websites handle a lot of personal data every day.
When the data collection is huge, so are the concerns for data privacy. Users are now more concerned about how websites are handling their personal data. Therefore, it is crucial that we delve into the realm of e-commerce and data privacy.
If you are an e-commerce store owner seeking ways to effectively manage your business while safeguarding the data privacy of your users, this article is for you.
Having that out of the way, let’s get started.
Privacy in eCommerce is a serious matter of concern, especially due to the bulk data it handles every day. A main reason for the rising concern about privacy in eCommerce is the emergence of a new technological environment in which data mining happens at a large scale.
This environment facilitates a large flow of data that helps businesses to offer better shopping experiences to their customers. But this also raises privacy concerns in eCommerce.
Governments have introduced various privacy regulations to give users control over their personal data shared on websites. Before the EU’s GDPR, many websites weren’t following fair information practices when handling user data. Only a few customers believed they had the right to control the data shared across eCommerce sites.
And then EU launched the General Data Protection Regulation in 2018, and it changed everything. It has become mandatory for websites to comply with GDPR guidelines and safeguard the privacy of the users. Many big companies were fined huge millions of Euros for GDPR violations.
The GDPR has brought up new dimensions to the privacy realm, and many websites have introduced their own versions of GDPR. We will discuss more about the global data privacy regulations in the later part of this article.
Technology for Surveillance
As mentioned earlier, technological advancements have made data mining easier for businesses. This technological environment has enabled companies to collect personal data from users through surveillance tools.
Businesses collect bulk data from users through different channels. These include data directly obtained from the consumers, such as personal information entered in a login form and billing and payment information entered at the time of purchase. Additionally, data is collected through website cookies and other tracking technologies.
These surveillance technologies provide businesses with the information they need for user profiling and analysis, helping them identify potential customers to sell their products. This has raised concerns about data privacy by users.
Technology for Privacy Enhancements
Privacy Enhancement Technology (PET) is a set of tools designed to enhance data privacy and protect users’ personal information. PET includes encryption methods, anonymization techniques, access control mechanisms, secure communication protocols, and privacy-preserving data collection and processing practices.
It’s fascinating to observe how technology can create a problem and its solution. An excellent illustration of this phenomenon is the interplay between Surveillance Technology and Privacy Enhancement Technology. While Surveillance Technology may compromise user privacy, PET emerges as the antidote.
For instance, websites often utilize cookies to gather personal data from users, but the implementation of cookie banners empowers users to control the sharing of their personal information. This shows how technological advancements can create privacy concerns while simultaneously giving rise to innovative solutions that prioritize user privacy.
Also Read: Privacy by Design (PbD): A Holistic Approach to Safeguarding Data Privacy
Now let’s see what are the different source points in which eCommerce websites collect personal data from users.
For every eCommerce website, there are different source points from which a website might collect information from users. The following are some common sources of data collection in eCommerce:

Account Registration
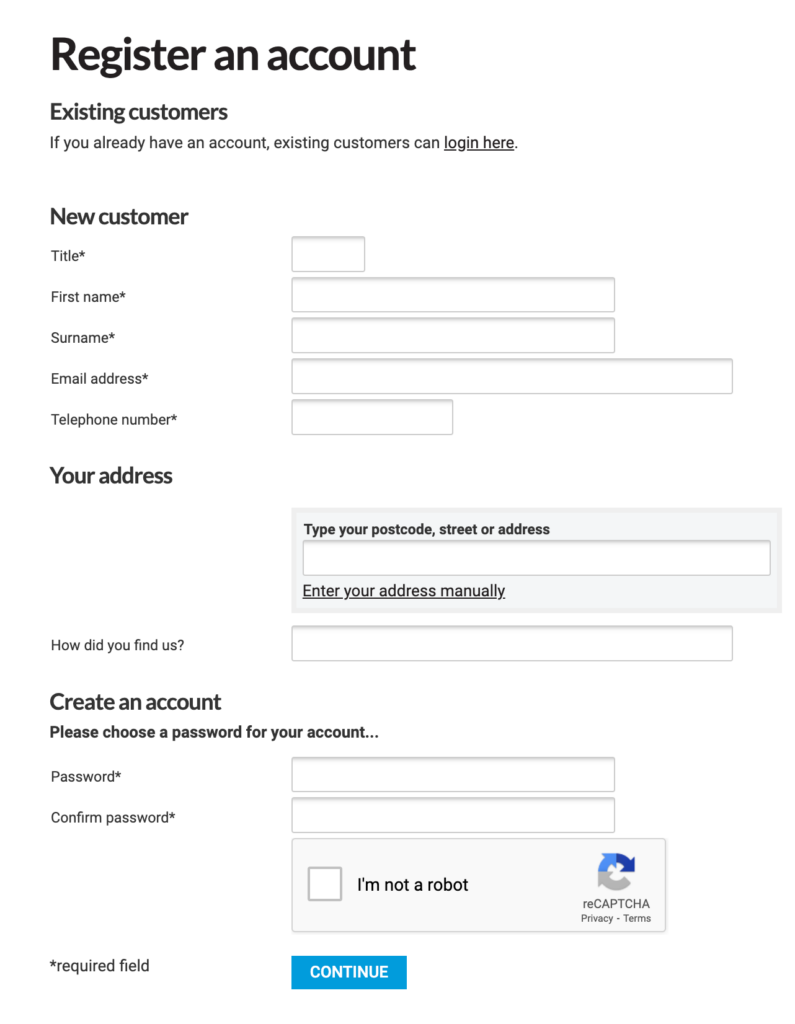
This is the initial stage of data collection in an eCommerce website. When a user registers an account with an eCommerce website, a variety of information is collected. This includes details such as the user’s name, email address, mobile number, gender, date of birth, and address.
These data points are typically gathered during the account creation process to establish user profiles and enable personalized experiences on the platform. But these are personally identifiable information that can be used to identify the user in person.
Analytical Tools
Every eCommerce websites use different analytical tools to track user interaction with their website and offer personalized suggestions and recommendations. This data can include IP addresses, device information, browsing patterns, session duration, clickstream data, and referring URLs.
The use of analytical data enables websites to understand users’ preferences better and improve the user experience and performance of their sites.
Purchase and Transaction
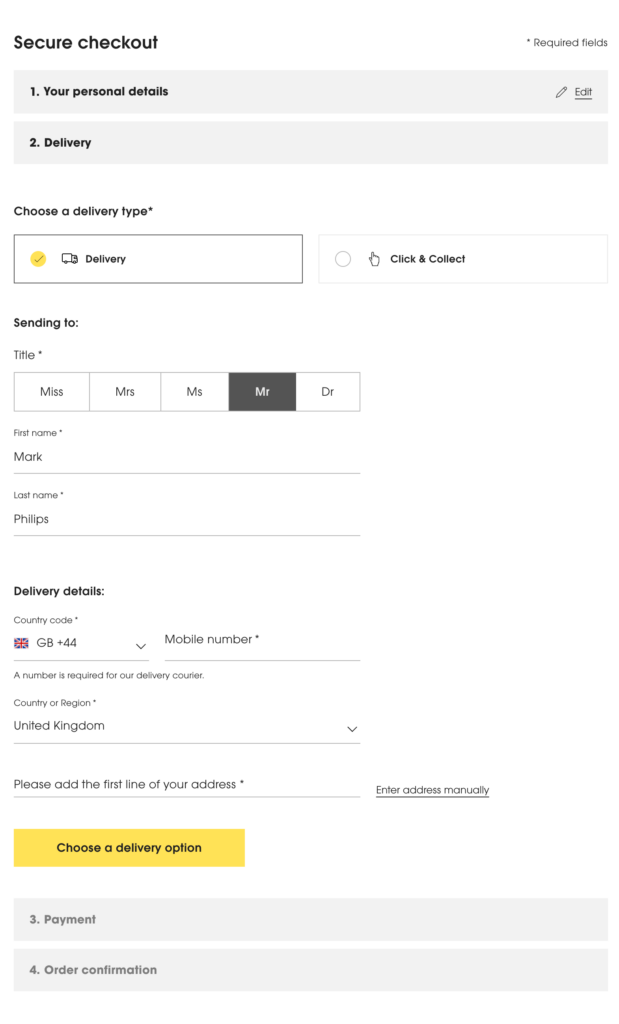
Users provide various information to websites while making purchases. This includes the necessary details for processing the transaction, as well as the billing and delivery information provided by the user. These data points are crucial for ensuring a smooth and efficient order fulfillment process.
Website Cookies
Website cookies are a major data collection source point in eCommerce. Cookies are used to track user behavior, remember user preferences, and personalize the shopping experience on the website. Data collected through cookies may include user preferences, browsing history, cart contents, and interactions with the website.
If you want to comply with major privacy laws for cookie usage on your website, try out our cookie consent plugin for WordPress.
Feedback and Reviews
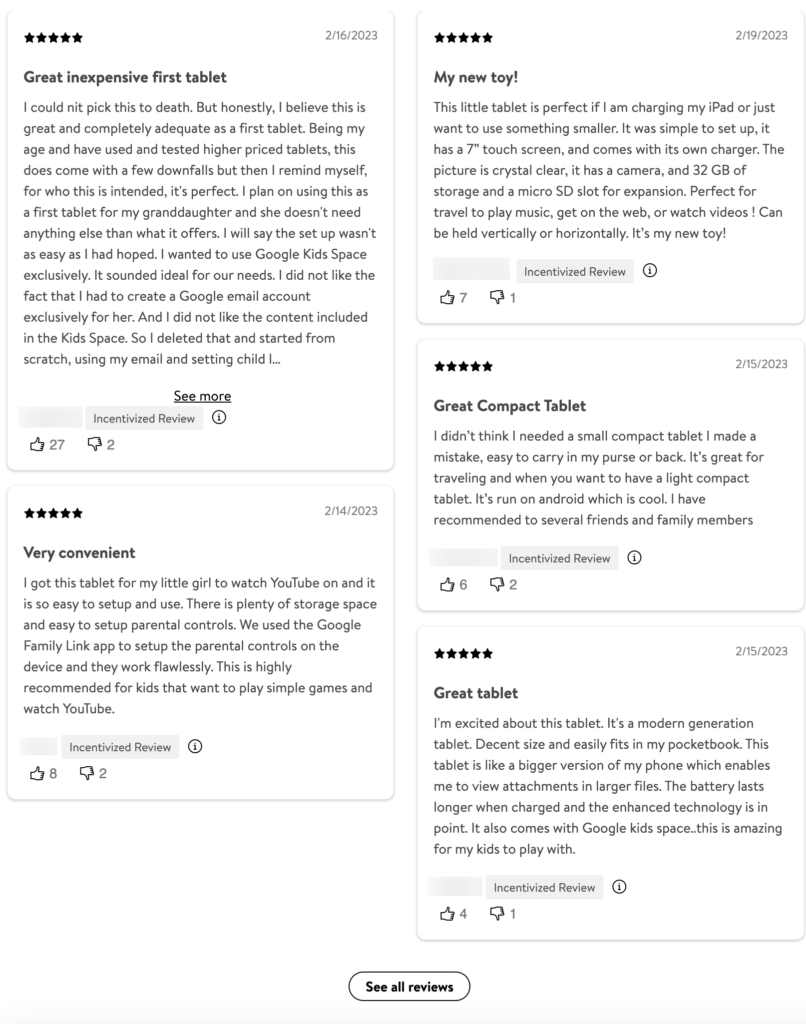
Customer feedbacks are important for any kind of business. eCommerce websites often collect customer feedback and reviews to promote their products and services. They showcase positive feedback and reviews to create social proof for their websites.
Customer Support Interactions
Many customers reach out to the Support team via Live Chat, Email, Phone, or Social Media. The conversation with customer support is often collected for internal purposes such as quality assurance, resolving issues, and improving customer service. This includes call recordings, chat transcripts, messages, etc.
Social Media Integration
Many eCommerce websites now allow users to connect with their Social media accounts to interact with their friends and family. In such cases, the websites will collect data such as social media profile information, friend lists, or social sharing activities.
An eCommerce website relies on different data collection source points to gather personal data from users. These sources include account registrations, purchase transactions, website analytics, customer support interactions, and more. It is evident that the collection of various user data is essential for the proper functioning of an eCommerce website.
By leveraging this data, eCommerce platforms can deliver personalized experiences, facilitate secure transactions, and optimize their overall operations.
So here comes the big question!
In the age of digital commerce, where data is more valuable than ever before, safeguarding data privacy in eCommerce is definitely a complex matter, but not impossible. In order to protect eCommerce customers’ data privacy, there are numerous challenges to overcome.
On the one hand, customers are becoming increasingly aware of the potential risks associated with sharing their data. On the other hand, websites need to collect personal data from customers to offer a personalized experience and enhance customer satisfaction. Balancing user experience and privacy concerns is a tough call for businesses.
Challenges for Data Privacy in eCommerce
Now, let’s discuss the major challenges that affect data privacy in eCommerce.
Data Collection
It is an obvious challenge for eCommerce businesses in terms of ensuring the data privacy of their customers. eCommerce websites heavily rely on large amounts of user data for proper functioning and offering personalized suggestions to their customers. A major part of this data includes PII (Personally Identifiable Information), so users are concerned about sharing their personal data with websites.
Data Breach and Security Risks
Since eCommerce websites handle the bulk amount of personal data, including the financial information of customers, they are often targeted by hackers to get access to sensitive information. Cybercriminals attack eCommerce websites for financial fraud and identity theft.
Also, they may send fake emails or create fake copies of websites to trick customers into revealing their sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card details. These are some of the common security threats that can compromise the data privacy of users.
Integration with Third-Party Services
eCommerce websites integrate various third-party tools and services on their websites. This integration helps them to offer a better shopping experience to their customers. Also, various analytical tools are used to get better insights into user behavior and interaction on their website.
It is really a challenge to ensure that these third-party services handle users’ personal data responsibly and adhere to privacy standards.
Global Regulatory Compliance
If you are selling internationally, you must be aware of the data privacy regulations of those countries. Many countries have strict privacy laws and require you to comply with these regulations. Upholding privacy standards and ensuring compliance with these regulations can present a significant challenge for eCommerce websites.
Lack of Awareness
The landscape of privacy regulations is constantly evolving, with new regulations continually being introduced. The lack of awareness regarding these regulations and a failure to prioritize user privacy pose significant challenges for many eCommerce companies.
eCommerce companies neglecting the value of user privacy is a big challenge in safeguarding privacy in eCommerce. This can lead to severe consequences in an era where privacy is increasingly valued and protected.
How to Overcome the Challenges of Data Privacy in eCommerce?
We have discussed the major challenges of data privacy in eCommerce. Now, let’s see how we can overcome these challenges.
-
eCommerce websites don’t function without data collection. But you can limit the data collection on your website. Limiting the data collection in checkout pages will optimize the checkout process and result in a faster conversion.
-
You should disclose what type of data is collected, how it is processed, and why it is collected. Keep your legal documents, such as privacy policy and cookie policy, up-to-date.
-
Protecting your website from security breaches is important. Install security firewalls and SSL/TLS encryption on your website. Do regular security checks and keep plugins and other software installed on your website up-to-date. Also, it is your responsibility to inform users in case a data breach happens on your website.
-
When integrating third-party services on your website, ensure they comply with the latest privacy standards and maintain up-to-date data protection measures.
-
Keep up-to-date with the latest data protection laws, such as GDPR, CCPA, and LGPD, and make necessary changes to your website.
While heightened privacy concerns may seem challenging for eCommerce businesses, you can use this opportunity to demonstrate your commitment to data privacy. By showcasing the measures you have in place to protect user data, you can build trust with your customers.
Global data privacy regulations play a significant role in safeguarding individuals’ personal information and shaping how businesses handle data. Here are some of the most prominent regulations:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The European Union introduced GDPR to protect the data privacy of EU users. It sets stringent rules for data protection, consent, and user rights. It emphasizes transparency, accountability, and the need for explicit user consent when processing personal data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Implemented in California, USA, CCPA grants consumers greater control over their personal information held by businesses. It requires businesses to disclose data collection practices, allow opt-out options, and provide mechanisms for data deletion upon request.
- LGPD (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados): LGPD is Brazil’s comprehensive data protection law inspired by GDPR. The law regulates the processing of personal data and grants users the right to have control over their data. It imposes obligations on businesses, including transparency and lawful processing.
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): PDPA was enacted in Singapore to govern the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data by organizations. It establishes consent requirements, data accuracy obligations, and data breach notification guidelines.
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): PIPEDA is Canada’s federal privacy law governing the private sector’s collection, use, and disclosure of personal information. It emphasizes consent, data accuracy, and individual access rights.
The above-mentioned are some of the popular data protection regulations in the world. Each regulation aims to protect individual’s privacy rights and imposes obligations on businesses to handle personal data responsibly. Businesses must stay informed about and comply with applicable regulations based on their operations and geographical reach.
Conclusion
Managing an eCommerce business is not an easy task. It involves constantly being up-to-date with the latest standards of the industry. Ensuring the data protection of your customers and site visitors is a part of it. By providing data protection measures and valuing the privacy of your customers, you can build customer loyalty and attract new customers.
This article was intended to help you understand the complexities of data privacy in eCommerce and let you know that ensuring privacy in eCommerce can be challenging but not impossible.
Thanks for reading!



