The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has been in effect for some time now, and it has significantly increased challenges for marketers, businesses, and advertisers. In this article, we’ll explore the impact of GDPR on marketing and how to comply with its requirements while maintaining effective marketing strategies.
Ever since its inception, GDPR has awakened to the importance of privacy standards, prompting many countries to enact similar data protection regulations. The landscape has become increasingly intricate for businesses operating within the EU, especially with the introduction of the Digital Markets Act and the forthcoming AI Act.
These regulations are adding layers of complexity for businesses, requiring marketers to diligently ensure compliance while effectively leveraging marketing tools. The good thing is that many advertising and marketing platforms have implemented changes to prioritize user privacy while still providing valuable insights to marketers.
This blog post aims to guide you in navigating GDPR regulations while continuing to gather insights on users and refine your marketing strategies.
Let’s dive in.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) regulates businesses handling personal data of EU citizens. It establishes several obligations for businesses to comply with and grants several rights to consumers to protect their personal data shared with businesses.
Any businesses that collect, use, or process the personal data of EU citizens have to comply with GDPR, or else they’ll face huge fines and penalties.
Here are the top reasons why GDPR is important in marketing:
Protect Personal Data
GDPR provides consumers with more control over their personal data shared with businesses. Marketing heavily relies on users’ data to make decisions to promote products and services. The data helps marketers identify how consumers are responding, how effective their campaigns are, and, more importantly, how to improve user experience.
GDPR requires websites to ensure the safety and security of the personal data of their users. They need to obtain consent before collecting or processing users’ personal data and then take steps to protect the data from unauthorized access or breaches.
If businesses have taken enough measures to comply with GDPR, then users can ensure that their data is safe, and they are more likely to engage with brands and share their information willingly.
Increase Transparency
GDPR requires businesses to be transparent about their data processing activities. Users have the right to know if their data is being processed, what specific data is collected, how it is processed, who has access to it, and how long it will be retained.
This increases transparency in data processing, and users can opt out of data processing at any stage at a granular level. They can continue sharing their data to improve user experience while opting out of marketing emails.
Build Trust
Even though marketers think GDPR compliance can only worsen their marketing efforts, it could actually benefit them in some ways. People are now more concerned about their privacy on the Internet. When a brand showcases itself as compliant with the latest privacy standards, this will build trust between businesses and consumers.
You can leverage GDPR compliance for your marketing campaigns to build trust and brand reputation for your business. This will make you stand out from the competition and be a reason for people to choose your brand over your competitors.
We have a detailed guide on eCommerce and digital privacy, that will help you understand more about how protecting data privacy is important for eCommerce businesses.
Better Data Protection and Security
GDPR requires websites to follow better data protection standards to ensure the personal data of their customers are protected. They need to implement additional security standards and regular risk assessments to mitigate any potential breaches.
Businesses have to update their data processing policies and procedures to comply with the standards of GDPR. For big corporates, hiring a Data Protection Officer (DPO) is important to address any privacy related issues.
Avoid Fines and Penalties
This is obviously an important reason why GDPR is important in marketing. If your marketing strategies involve collecting or processing information from your customers, as they likely do, and you are not complying with GDPR guidelines, then you may face fines up to €20 million or 4% of your company’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
So, in short, GDPR compliance is not a choice but a legal obligation for businesses operating within the EU or handling the personal data of EU citizens.
1. Processing of Information
Marketing heavily relies upon information from users. It helps marketers make better decisions and improve customer experience. However, GDPR mentions six legal bases for processing personal information from users.
Businesses can only process information from users if it falls under these six legal bases: consent, contract, legal compliance, the vital interest of the user, public interests, and legitimate interests.
- Consent: Businesses can process the personal information of their customers if they have obtained explicit consent from them. The consent should be freely given, informed, and obtained with a clear, specific action.
- Contract: Processing of personal information is allowed if it is required to fulfill a legal contract between the business and the customer.
- Legal compliance: Businesses can process personal information if it is required for compliance with legal obligations.
- Vital interest of the user: Businesses can process personal information if it is necessary to protect the vital interests of the user.
- Public interest: Processing of personal information is allowed for reasons of substantial public interest, as authorized by EU or national law.
- Legitimate interest: Businesses can process personal information if they have a legitimate interest in processing the data, but it shouldn’t override the privacy rights and freedom of data subjects.
Among these, consent is the primary legal basis for marketers to process customer data. GDPR also mentions how consent should be obtained from users. Refer to this guide to learn more about consent requirements as per GDPR.
2. Data Rights and Management
GDPR grants data subjects eight rights to protect their personal data. Marketers collecting personal data from users are required to honor these rights and provide options for users to exercise them.
The rights of data subjects that you should consider for marketing activities:
- Right to be informed: Users should be informed about the purpose of collecting their data, how it is used, who else has access to it, and how long it will be retained. Marketers can obtain consent only after disclosing these details to the users; then, only the consent will be valid.
The principles of GDPR also enforce purpose limitation, which means businesses cannot use the personal data of their customers for purposes other than those for which they consented.
For example, if a user shares their email address for an invoice, marketers cannot use it for email marketing without separate consent.
- Right to access data: GDPR entitles users to access the data held by marketers. Upon request, marketers are obligated to share the collected data in a readable format.
- Right to rectification: Users retain the right to rectify any inaccuracies in their personal data held by businesses. Marketers must promptly update their records across all databases upon receiving such requests. Any shared data with third parties must also be accurate and up-to-date.
- Right to be forgotten: Users can request the deletion of their personal data held by businesses. Upon receiving the request, any data related to the user should be removed from the database.
After deleting the if a user still receives any marketing emails from a company, it is considered as a violation of GDPR.
- Right to restrict processing and automated decision-making: Users have the right to restrict the processing of their personal data by businesses, thereby preventing its use for any form of processing, including marketing.
Also, if marketers are using any profiling tools or automated software to segment users and make automated decisions related to their interactions with the website, users should be informed about the automated decision-making process and obtain their explicit consent for processing their personal data for automated decisions
To honor these rights, marketers need to take additional steps and manage the personal data of users accordingly.
3. Efforts for Implementing GDPR Compliance
Achieving GDPR compliance is not a simple task. It requires a lot of effort and time. This could slow down marketing efforts and potentially affect the results they bring to the table. Each member of the marketing team should take more responsibility to ensure that their contribution is aligned with GDPR guidelines.
Businesses need to appoint data protection officers and consult legal persons to ensure compliance with GDPR. They should also conduct proper risk assessments and data audits regularly to find any potential threats or loopholes that could risk their compliance.
4. Cost of Compliance
Implementing and maintaining GDPR compliance adds many expenses. These might involve hiring data protection officers, purchasing compliance management software, and conducting privacy audits. These initial costs can strain marketing budgets, especially for smaller companies.
5. Contextual Marketing
As GDPR restricts personalized marketing based on users’ profiles, marketers are focusing on contextual advertising based on the content users are browsing. This helps marketers identify when and where their target audience is most receptive to their messages, allowing them to allocate their resources more efficiently and maximize the impact of their marketing campaigns.
Here are some general guidelines that will help you achieve GDPR compliance for your marketing campaigns.
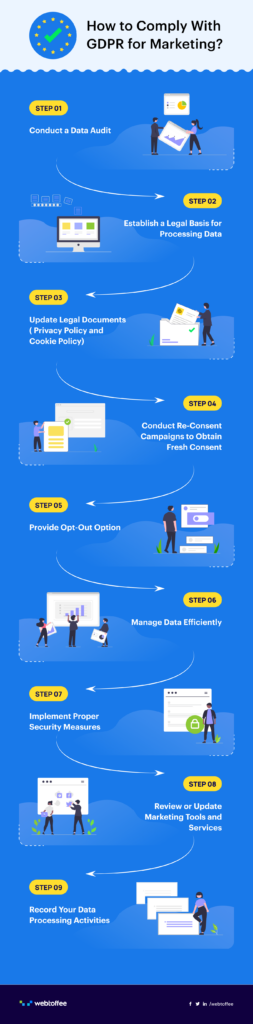
Conduct a Data Audit
Do a complete audit of the data collection practices for your marketing campaigns. Identify all the points where customer data is gathered, including lead generation tools, email subscription forms, and third-party apps and services.
Additionally, your website may use third-party cookies or tracking scripts to monitor users’ activity on your website. Since cookies do collect information from your site visitors, you should be aware of the cookies used on your website and their purpose.
Check out our guide on “How to Identify Cookies Your Website Installs on the Browser?” for more information.
Establish a Legal Basis for Processing Data
Once you have identified the details of the data you collect and its purpose, you should establish a legal basis for collecting and processing the data. Consent serves as the primary legal ground for marketers to gather personal data.
You should inform users about the data collection, its purpose and retention period. Since GDPR requires an opt-in consent mechanism, you should obtain explicit consent from your customers with clear action, such as clicking an accept button or checking a checkbox. Implement the opt-in consent option on all your data collection source points.
For cookies, you can create a cookie banner on your website to obtain and manage consent for cookies.
Update Legal Documents
Update your legal documents, such as your privacy policy and cookie policy, to disclose the processing of personal data on your website. GDPR requires you to add several details to your privacy policy, such as how the data will be used and who has access to it—including third parties like advertisers.
You should also mention how users can exercise their privacy rights, such as data deletion or data access.
For cookie policy, list all the cookies used on your website and their purpose. Also, provide users with the option to manage their consent preferences.
Check out the articles below to create a GDPR-compliant cookie policy and privacy policy for your website:
Requirements for a GDPR Compliant Cookie Policy
Privacy Policy Template: How to Draft a Privacy Policy for Your Website?
Re-Consent Campaigns
If you already have a database of users’ personal data, you need to conduct re-consent campaigns to get fresh consent; otherwise, you can’t use the existing data for your marketing campaigns.
By getting fresh GDPR-compliant consent, you can continue marketing to interested contacts without worrying about legal issues.
Provide Opt-Out Option
Allow users to unsubscribe from marketing emails and newsletters. Make the opt-out option easily accessible on your website. It should be straightforward and require minimal steps.
e. Avoid employing deceptive tactics or dark patterns to obscure the unsubscribe option. This is clearly against GDPR guidelines.
Manage Data Efficiently
Manage the personal data obtained from users efficiently. Only collect the minimum data required for processing your marketing campaigns. Always use IP anonymization whenever possible. Honor the rights of data subjects and follow the principles of GDPR to efficiently handle personal data for marketing purposes.
Implement Proper Security Measures
While implementing measures at the website level is crucial for data security, marketers must also safeguard personal data used for marketing against unauthorized access or breaches. Furthermore, it’s essential to provide thorough training to your marketing team members to handle data subjects’ personal information with care and responsibility.
Review or Update Marketing Tools and Services
You may be using various tools and third-party services for your marketing campaigns. Review these tools and ensure that they are GDPR-compliant. Also, update to the latest version of these services.
For example, Google has released an updated version of its analytics tool, Google Analytics (GA4), which prioritizes privacy and includes additional features for GDPR compliance. Similarly, make sure all other tools, such as your lead generation software, email marketing service, etc, are GDPR compliant.
Record Your Data Processing Activities
Maintain a record of your website’s data processing activities. This will help you proactively identify areas for improvement and ensure your website operates within GDPR guidelines. It helps prevent potential issues that could risk your compliance.
Also, keep a record of the steps you’ve taken toward GDPR compliance. This serves as evidence of your commitment to data privacy and can help you address any disputes or regulatory inquiries.
These are some general guidelines that will help you comply with GDPR for marketing. We strongly recommend that you consult with your legal advisor to ensure full compliance with the law.
Below are some of the biggest GDPR fines handed out so far:

1. Meta – €1.2 billion
The tech giant Meta was fined €1.2 billion for transferring data between the EU and the US. The Irish Data Protection Authority imposed the fine on 12 May 2023. This is, so far, the biggest fine under GDPR.
2. Amazon – €746 million
On 16 July 2021, Luxembourg’s National Commission for Data Protection (CNPD) fined Amazon a hefty €746 million for violating the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). CNPD found that Amazon wasn’t transparent about using customer data for advertising purposes.
3. TikTok – €345 million
On 09 September 2023, Ireland’s Data Protection Commission (DPC) fined TikTok for a series of GDPR violations in handling the personal data of Children.
4. WhatsApp – €225 million
WhatsApp was fined €225 million by Ireland’s Data Protection Commission (DPC) for violating GDPR guidelines on transparency in data processing on 02 September 2021.
5. Google – €90 million
The French Data Protection Authority fined CNIL €90 million on 31 December 2021 for not allowing users to refuse cookies on Google and YouTube.
Source: GDPR Enforcement Tracker
Frequently Asked Questions
Is GA4 GDPR Compliant?
No. Google Analytics is not GDPR compliant by default. However, GA4 has implemented additional privacy features that will help you comply with GDPR.
Refer to this article for more information: How GDPR Affects Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager? All You Need to Know
What Is Google Consent Mode v2?
Google Consent Mode v2 is an updated version of the Google Consent Mode, which is an API developed by Google to control Google tags based on users’ consent preferences. It will interact with the website’s consent management platform (CMP) and send the consent signals to Google.
The GCM v2 is a privacy-focused update that offers improved transparency and control to users over their personal data shared with businesses.
Check out our detailed article on Google Consent Mode to learn more about it.
What Happens if You Don’t Comply With GDPR?
Failing to comply with GDPR can result in serious consequences for businesses. The fines for non-compliance can be up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Additionally, non-compliance with GDPR can lead to reputational damage for businesses. Negative publicity surrounding data breaches or violations of privacy rights can affect customer trust and loyalty.
How Does GDPR Affect Email Marketing?
GDPR significantly impacts email marketing by requiring marketers to obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personal data. Marketers should be transparent about their data collection practices and provide clear privacy notices to users.
Also, allows users to easily unsubscribe from marketing emails. This could also affect the open rate of marketing emails.
Conclusion
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) establishes several obligations for marketers when handling personal data of users. If your operations extend to the EU, you likely have already implemented measures to meet GDPR standards. For those considering expanding their business to the EU, complying with GDPR is not an option but a legal requirement.
We hope this article has provided you with insights on how to comply with GDPR for marketing. If you have any queries, please drop them in the comments. We’d be happy to help you.



