This blog post covers everything you need to know about cookies – what they are, how they’re used, and how they work.
Cookies are small pieces of information created by web servers and placed on a user’s browser when they visit a website. These cookies carry various information such as user activity, site preferences, cart data, session data, etc.
Cookies may contain personally identifiable information of a site visitor and can be used to track or identify a person using the internet. If you are interested in learning more about cookies and how they are used, you’ve come to the right place.
So without further ado, let’s get started.
The term cookie was coined by Louis J. Montulli in 1994 and was originally derived from the term magic cookie, which was already being used in computing technology at that time.
A magic cookie is an old computing term used to refer to a packet of data a program receives and sends back without any changes. It was used by Unix programmers to identify an event between two programs.
Montulli was working for Netscape Communications and was assigned to develop an eCommerce application for MCI WorldCom, a popular telecommunications company in the 90s (later acquired by Verizon Communications).
The company wanted to reduce its server load by not retaining partial transaction states and asked Netscape to find a solution to store the data in the client’s computer. This led to the development of cookie technology.
The first set of cookies was used to identify whether a user had already visited the website. Later in the year 1995, Internet Explorer released version 2 with the support of internet cookies.
Since its inception, cookies have undergone various developments. Now there are different types of cookies based on their source, purpose, and expiry.
The following are the major types of cookies used by websites:
1. Session cookies
Session cookies are short-term cookies that stay active on the users’ browsers only during their session on the website. Once a user closes the browser, the session cookies will automatically be removed from the browser.
Session cookies are mostly used by eCommerce websites to keep the product in the cart available for the users while they look for other products.
2. Persistent cookies
Persistent cookies are used by websites to remember information about the site visitors. They normally do last for a longer period of time when compared with session cookies. However, many data protection laws restrict the use of persistent cookies for longer than six months.
Persistent cookies can be used to save the login information of a user so that they don’t have to enter it each time they visit the website.
3. First-party cookies
First-party cookies are cookies loaded by the website visited by the user. They are generally used to improve the user experience of the website.
For example, websites use first-party cookies to remember the preferred language settings of a user. So the next time the user visits the website, it loads the website in the preferred language.
4. Third-party cookies
Third-party cookies are loaded by third-party services and tools used on a website. They are mostly used for advertising, analytics, or tracking purposes. Third-party cookies collect information on a user’s activity on the website and share them with advertisers to show relevant ads and personalized suggestions.
For example: After searching for watches on Amazon, you see suggested ads on your social media platforms. Third-party cookies are responsible for this.
What are the Functions of Cookies?
Websites use cookies for various purposes, such as advertising, marketing, analytics, etc.
The following are the three major functions of cookies:
1. Improve User Experience
Most websites use cookies to improve user experience on their website. Cookies are used to “remember” users during their active sessions or repeated visits. They collect information on users’ activity on the internet and use this information to load the website as preferred by the user.
For example: When a user visits a multilingual website for the first time and selects French as the preferred language. The next time he visits the website, the website will automatically load information in French. Similarly, cookies store information on login activities, user credentials, etc.
2. Advertising and Marketing
We have already discussed the third-party cookies used on a website. Third-party cookies mostly serve the purpose of showing relevant ads to users depending on their website activities and preferences.
Advertisers use the information from third-party cookies to identify potential customers for their products or services. This enables the showing of relevant ads to a targeted audience.
Another use of cookies in advertising is for retargeting purposes. Retargeting, or remarketing, is an online advertising strategy to show ads to visitors who have already visited the website.
For example: When you visit Honda Motor Company’s website to look for your dream car, and later you see ads from Honda is because of retargeting. This is an efficient marketing strategy as advertisers can show ads to users who already have shown interest in the products.
3. Analytics and Website Optimization
Cookies can be used for analytical purposes and website optimization. Websites use cookies to get information about the site visitors. These include information such as demographics, geo-location, etc.
Cookies help websites to :
- identify friction factors
- analyze the time taken to proceed to checkout
- evaluating the effectiveness of CTA placements and button positioning
Also Read: TikTok Pixel and GDPR Compliance: All You Need to Know
How do Cookies Work?
Cookies are tiny bits of data that websites use to remember some things about site visitors. When a user visits a website, the server loads the webpage on the browser and saves cookies on the browser. When the user revisits the same website, the browser sends back the cookies to the server to identify you as the same user who visited early.
This helps websites to remember the site visitors and their preferences on their website. Once the server identifies the user, it sends the webpage as preferred by the user. (language preferences, product recommendations, etc.)
As you can see, there are a lot of data exchanges happening between the server and the browser. These activities are totally invisible to the user unless they have set preferences to get alerts when a website loads cookies on their browser.
How do Cookies Affect Data Privacy?
Usually, cookies are not designed to intrude on your data privacy, but since the cookies carry a lot of information about a user, it has a potential threat of exposing the identity of a user over the internet. Cookies carry information like IP address which can be considered as PII (Personally Identifiable Information).
Also, many users find it to be annoying to see personalized ads when visiting websites. Another concerning factor is tracking cookies which are used to help businesses identify their target users and their interest. They keep track of user activity on the internet, which can be intrusive in certain cases.
So even though cookies are not designed to harm data privacy, it carries a potential risk to users’ privacy in the digital space.
What are Cookie Laws?
Cookie laws are privacy legislations that require websites to get consent from users before loading cookies on their browsers. There are hardcore privacy laws like GDPR that give users more control over their personal data. These laws are designed to protect users’ privacy in the digital space.
Websites require prior consent from users to use cookies. Users have the right to revisit their consent and ask websites to send a copy or delete information about them. If a website fails to comply with these regulations, heavy penalties are imposed on them for noncompliance.
These regulations and legal requirements may change according to different laws and the place you are residing, but there are many data privacy laws across the world, and we can expect more in the future.
Read our detailed articles on different privacy laws:
Five Years of GDPR: A Look Back at the Impact of the EU’s Data Protection Law
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and Cookies: What you need to know
Saudi Arabia Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL): An Overview
Although some cookies are essential for websites to function properly, you can block third-party tracking cookies on your browser. Let’s see how you can block cookies on different browsers:
Block Cookies on Google Chrome
- Click on the three vertical dots in the upper right corner near your profile icon.
- Go to the Settings menu.
- Once you are on the Chrome Settings page, go to the Privacy and security tab and select Third-party cookies.
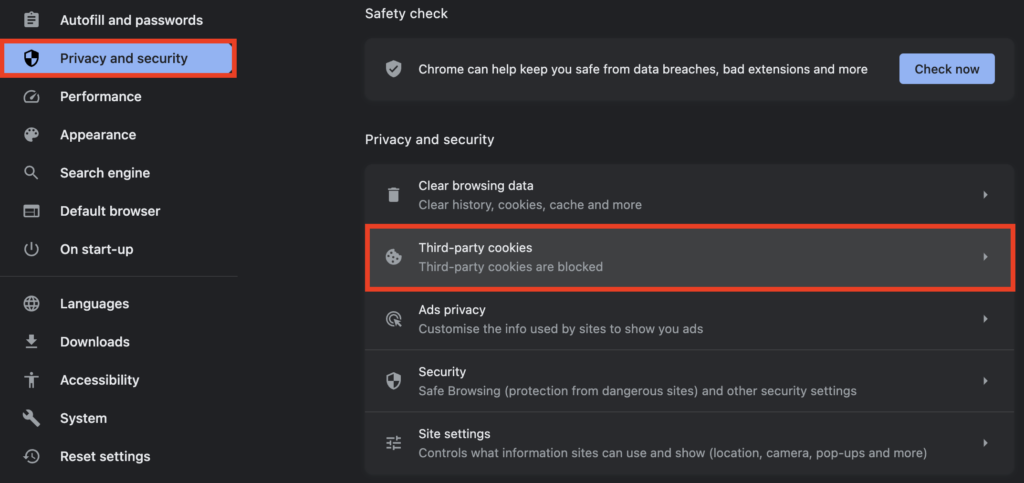
- Click on the Block third-party cookies radio button to block cookies. Additionally, you can enable the Send a ‘Do Not Track’ request with your browsing traffic checkbox.
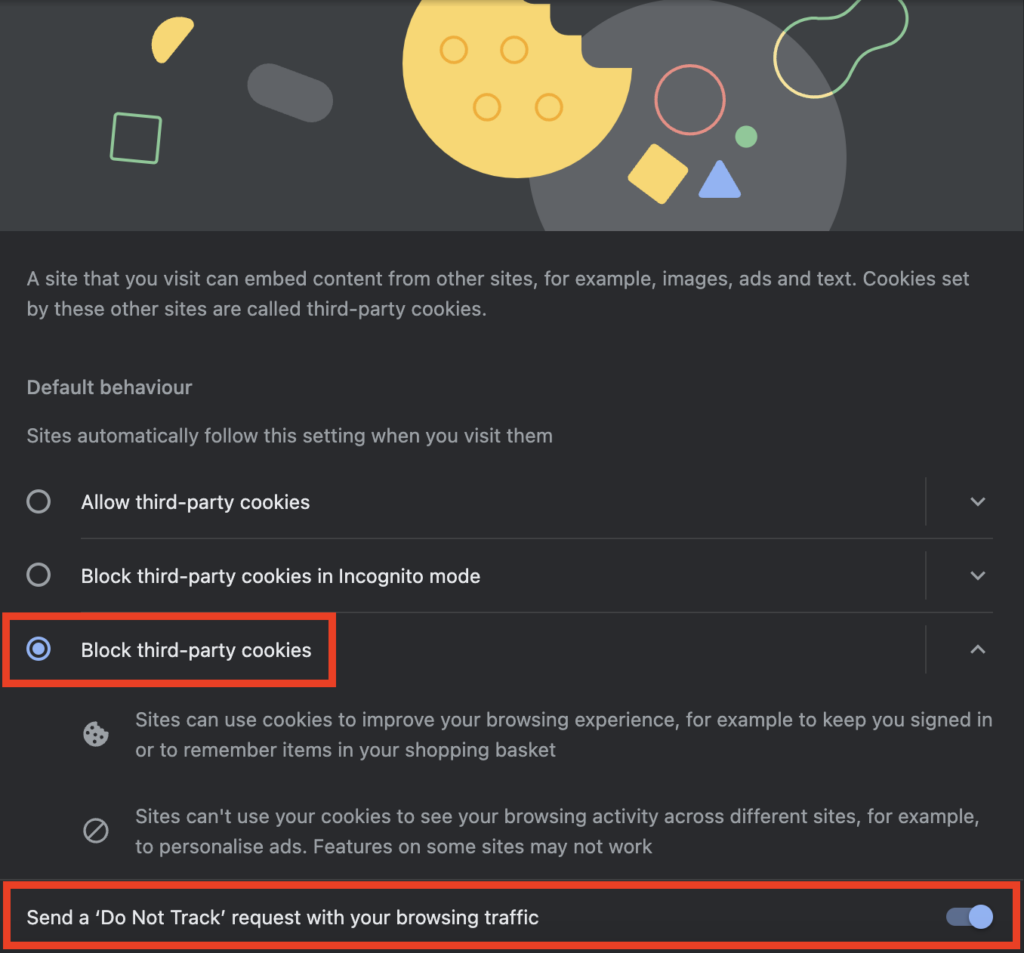
Block Cookies on Safari
Safari, by default, blocks third-party cookies. However, you can ensure it from the following steps:
- Go to Safari > Settings from the top menu bar.
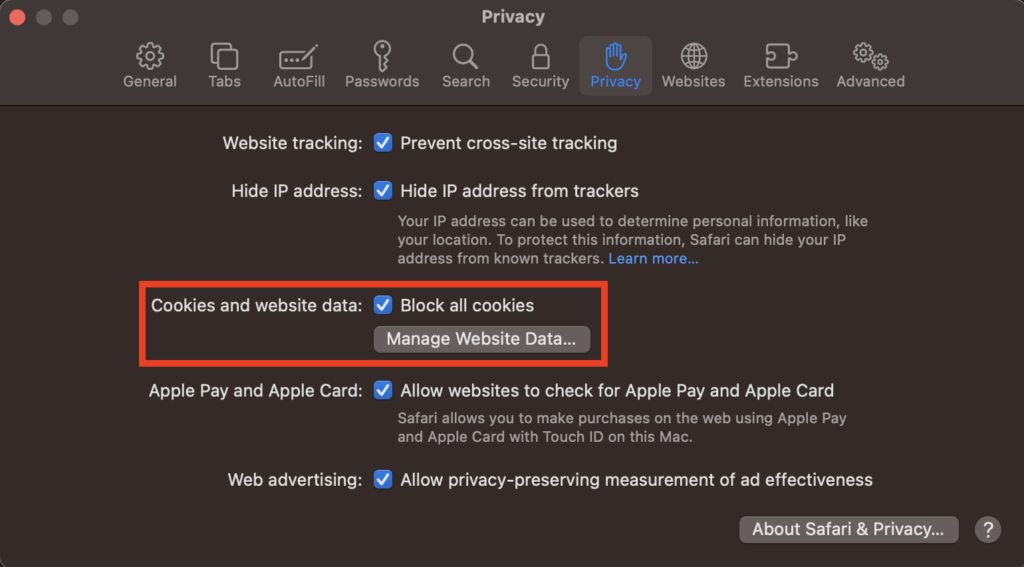
- Enable the Block all cookies checkbox.
Block Cookies on Firefox
Firefox offers three types of privacy settings for users; Standard, Strict, and Custom. In all three settings, third-party cookies will be blocked by default. However, the Custom option allows you to choose the specific type of cookies to load.
- Go to Firefox> Settings from the menu bar.
- Select the Privacy & Security tab.
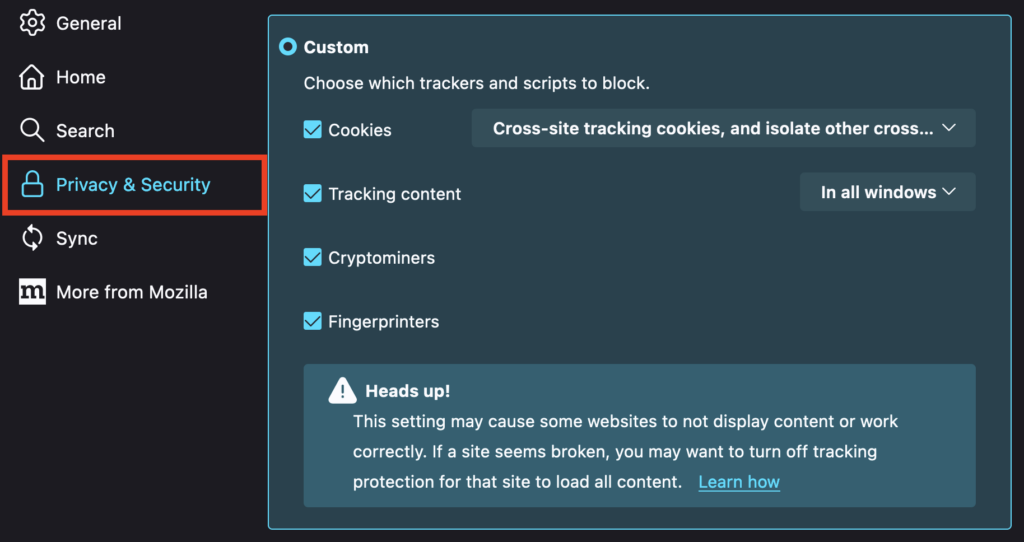
- Choose the Custom option and select the trackers or scripts you want to block.
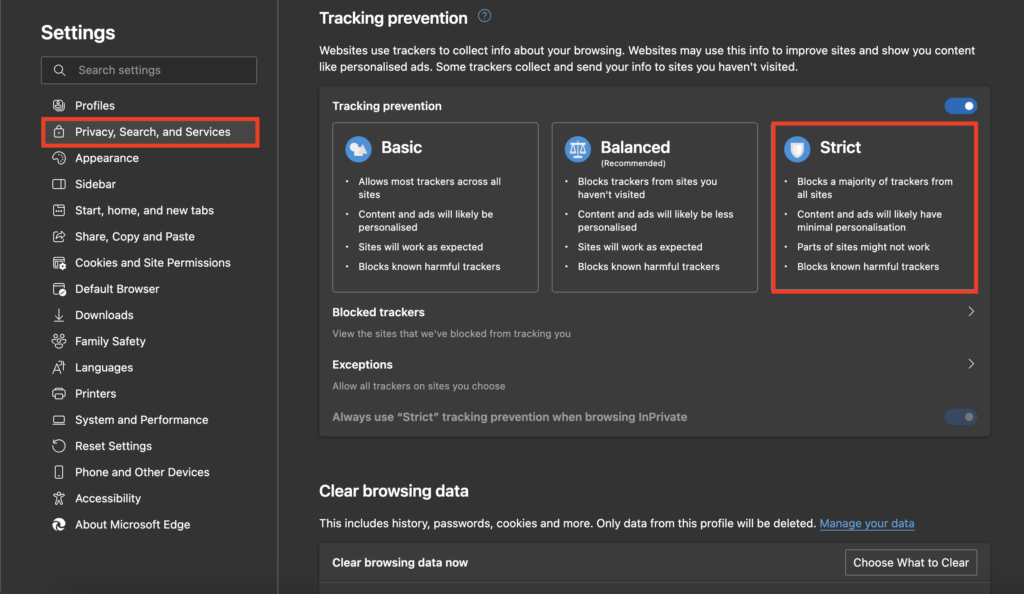
Block Cookies on Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge offers three levels of privacy settings; Basic, Balanced, and Strict. Among these, Strict is the one with the most security and blocking.
Click on the three horizontal dots near your profile icon and select Settings.
Go to the Privacy, Search and Services tab and select Strict under Tracking Prevention settings.
Popular Terms Associated with Cookies
Now let’s discuss the popular terms associated with cookies.
Zombie cookies are cookies set by third parties which are permanently installed on a user’s computer. They cannot be deleted from the computer, as they will regenerate themselves after being deleted. (that’s why the name “zombie”). Zombie cookies are capable of bypassing any restrictions of blocking set by the user.
They are used by advertisers or trackers to track individuals’ activity on the internet. Websites may also use zombie cookies to ban users from accessing the website.
Super cookies are like tracking cookies, but they aren’t really cookies; they are similar but worse. They are designed to be stored on the user’s computer permanently. Super cookies are installed into the HTTP header to collect data about a user’s browsing history and habits.
They are invincible and hard to find or remove from the user’s computer. So they have raised many privacy concerns.
The Interactive Advertising Bureau’s Transparency and Consent Framework (IAB TCF) provides guidelines for advertisers and publishers on how to use cookies for showing ads and personalized suggestions while complying with GDPR.
IAB introduced the TCF guidelines to help advertisers be responsible when handling the personal data of users.
Check out our detailed guide on IAB TCF: IAB TCF for WordPress
What Businesses Should Do About Cookies?
Businesses should first identify the cookies used on their website. Then inform site visitors about the cookies used and their purpose, duration, etc. Businesses should then obtain prior consent from users using a cookie banner or popup. Also, provide users with the option to revoke the consent at any time.
Here are some additional measures businesses should take:
- Display cookie consent banners in user-preferred language
- Block third-party cookies till the user gives consent
- Keep a cookie consent log
- Create a cookie policy to disclose cookie usage
How GDPR Cookie Consent Plugin Can Help?
If you are a website owner looking for cookie compliance for WordPress websites, a Consent Management Platform (CMP) like the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin can help you. The plugin offers everything to help you manage cookie usage on your website. It lets you create a cookie banner on your website and provide users with the option to accept or reject cookies.
You can scan and list all the cookies used on your website and display them on your cookie policy. The plugin supports major privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, CNIL, LGPD, etc. You can configure the cookie banner to show only to visitors from the EU region. Additionally, you can create a detailed consent log report as proof of compliance.
Also Read: Why Do You Need a Native WordPress Consent Management Plugin?
Conclusion
Cookies play a crucial role in enhancing user experience, enabling personalized advertising and marketing strategies, as well as aiding in analytics and website optimization. Despite how good they are at improving the user experience, there are concerns related to data privacy, especially with third-party and tracking cookies.
Businesses can use a consent management platform for their website to ensure compliance and manage cookie usage on their website. Implementing tools like the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin simplifies this process, allowing website owners to create cookie banners, manage consent, and uphold privacy standards.
Did you find this article to be informative? Drop your thoughts in the comments.
Thank you for reading!




Comments (2)
xing huang
August 22, 2023
hey,webtoffee。I purchased your (PayPal Express Checkout Payment Gateway for WooCommerce) plugin. But because my company is registered in China, I can’t use paypal’s credit card payment and pay later. I have applied for a refund several times, but no one has contacted me and responded to me, what is going on?
Hema
August 23, 2023
Hello Xing,
Thanks for reaching out. Our support agents have responded to your refund request. You may check your spam folder if you haven’t received the response yet. We would also like to inform you that the refund will be processed within the next 2-3 business days.