This article is a comprehensive guide to tracking cookies on a website. We’ll explain what tracking cookies are and how they affect your business. Whether you’re already familiar with them or just getting started, we’ll break down everything you need to know and share tips on how to handle them for your online activities.
Tracking cookies helps advertisers and marketers to provide personalized content and targeted ads. They collect personal information from website visitors and use this information to deliver content based on user’s preferences and browsing behavior.
However, the use of tracking cookies has raised concerns regarding user privacy. People are becoming more aware of their privacy rights, and many nations have introduced strict data privacy laws to protect the privacy of users in the digital space.
In this article, we will give you a detailed guide on tracking cookies. If you’re a website owner, you’ll discover how to effectively utilize tracking cookies on your website while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
For end-users, we’ll offer insights into tracking cookies and provide guidance on how to manage and safeguard your online activities by deleting or blocking them.
So, now we have set the context, let’s dive in.
What Are Tracking Cookies?
Tracking cookies are small text files that websites place on a user’s browser to collect data and track their activities. These cookies track users’ activity and process this information to help websites show personalized recommendations and targeted ads.
Tracking cookies collects information such as shopping preferences, device specifications, location, and browsing behavior. This information is used for gathering website analytics and showing targeted advertisements.
What Are the Different Types of Tracking Cookies?
We can classify tracking cookies into two categories: first-party tracking cookies and third-party tracking cookies.
First-party tracking cookies: First-party tracking cookies are those cookies set by the website owner on a site visitors’ browser when they interact with the website. Website owners use these cookies to collect information about the site visitors’ activities on their website. This helps to track users’ online behavior, their interactions, preferences, etc. It also helps in getting insights into clicks, impressions, and bounce rates.
Third-party tracking cookies: Third-party tracking cookies are cookies set by third-party services on the website you are browsing. These cookies are used by advertisers, marketers, and external services using display ads, social media plugins, etc.
Websites often include external resources such as social media widgets or analytics tools from third-party providers. These resources are loaded onto the website using HTML tags or JavaScript code provided by the third-party service. When users visit the website, their browser also loads these external resources, which will set the third-party cookies.
How Do Tracking Cookies Work?
Tracking cookies works by storing a unique identifier on a user’s web browser as they navigate different websites. These unique identifiers contain a string of letters and numbers and are created by websites or third-party services.
When a user visits a website that uses tracking cookies, the website’s server sends a cookie to the user’s browser, which then stores it locally on their device. When the user revisits that website, their browser sends the stored cookie back to the server.
This enables websites to recognize returning users, track their activities, and gather information such as browsing history, preferences, and interactions.
What Information Does Tracking Cookies Collect?
Tracking cookies collects different types of information from website visitors to personalize content, improve user experience, and facilitate targeted advertising.
This includes:
- Browsing history: Tracking cookies collect information about websites visited by users, including the pages viewed and the session duration.
- Preferences: These cookies gather data on user preferences, such as language settings, font size preferences, etc.
- IP address: Tracking cookies collect users’ IP addresses, which provide information about their approximate geographical location and internet service provider.
- Interactions: Tracking cookies monitor user interactions with websites, including clicks, scrolls, and form submissions.
- Shopping history: Tracking cookies track users’ online shopping activities, including product views, additions to cart, and past purchases.
- Device specifications: Tracking cookies collects data on the user’s device, including device type, operating system, screen resolution, and browser version.
These are some common types of data collected by tracking cookies. However, it depends on various factors, such as the website’s functionality, the types of cookies used, the website’s cookie policy, external services used, and the users’ consent.
How Do Websites Use Tracking Cookies?
Let’s explore a bit more about how websites use tracking cookies.
Personalized Content
Websites use tracking cookies to deliver personalized content to users based on their preferences and browsing behavior. This includes customized product recommendations on eCommerce websites, personalized movie shows by streaming platforms, etc.
User Authentication
Tracking cookies helps websites recognize returning users and remember the user credentials for authentication. This enhances user convenience and facilitates seamless access to account features and personalized content.
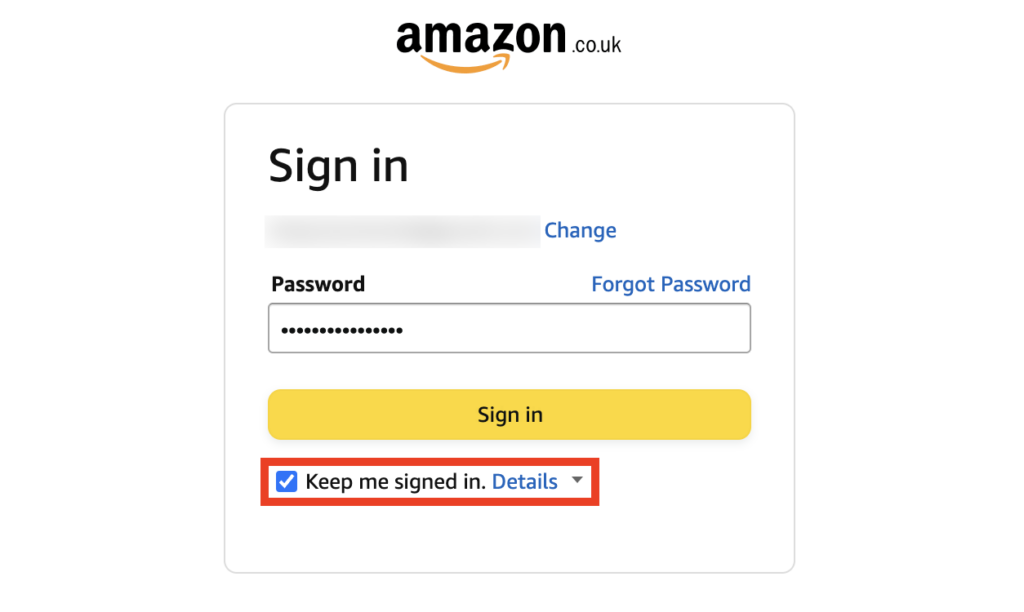
When you choose the “Remember Me” or “Keep me logged in” option on a website, a cookie is often set in your browser to store your login credentials securely. This allows the website to recognize you and automatically log you in the next time you visit without requiring you to re-enter your username and password.
Website Analytics
Websites use tracking cookies to gather analytics and insights on users’ interactions with the website. This includes user engagement, navigation patterns, heatmaps, etc. This helps website owners to optimize their sites for a better user experience.
Targeted Advertising
This is one of the most controversial uses of tracking cookies by websites. Websites use tracking cookies to show targeted advertisements to users. They track users’ online activities across different websites to build profiles and deliver personalized advertisements based on their interests, demographics, and browsing history. This allows advertisers to target specific audiences with relevant ads, potentially increasing ad engagement and conversion rates.
Remarketing Campaigns
Websites use tracking cookies to show ads to users who have previously visited their site but did not complete a desired action, such as making a purchase. By retargeting these users with relevant ads, websites can encourage them to return and complete the purchase.
Website Customization
Tracking cookies are also used to customize the user experience based on their location, device type, or language preferences. This includes displaying localized content, optimizing the website layout for different devices, and providing translated versions of the website.
Are Tracking Cookies Dangerous?
Tracking cookies are not necessarily dangerous, but it raises some serious privacy concerns. You may have noticed ads on your social media platforms that seem directly related to recent searches on sites like Amazon, which can understandably make users feel uneasy about their privacy.
Tracking cookies can create digital footprints of users’ online activities. It leaves behind a trail of information that could lead to track and identify the user. Moreover, they may contain personally identifiable information, posing a risk to users’ privacy and security.
When used responsibly, tracking cookies can be beneficial for both website owners and visitors. It helps websites to show personalized recommendations and gather valuable website analytics. Additionally, they enhance user experience by allowing visitors to view content according to their preferences and conveniently save login information.
Privacy Laws and Tracking Cookies
We have already said that tracking cookies may carry personally identifiable information such as IP addresses, so it raises some privacy concerns. Let’s have a look at major privacy laws and their provisions regarding tracking cookies.
GDPR and Tracking Cookies
As per the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation, websites using tracking cookies should obtain explicit consent from site visitors before loading them into their web browsers. The consent should be freely given, specific, informed, and with clear affirmative action.
GDPR also gives users the right to withdraw their consent at any time. So, website owners should provide users with the option to manage their consent preferences.
Also, it is important to state the purpose and the details of the cookies used on the website. If you are a website owner, you can use any consent management platform to create a GDPR-compliant cookie banner on your website. Using a cookie banner, you can disclose the use of cookies and provide users with the option to manage their consent preferences.
Check out our detailed guide on GDPR compliance for WordPress websites: A Complete Guide to WordPress GDPR Compliance
CCPA and Tracking Cookies
The California Consumer Privacy Act requires an opt-out consent mechanism for using cookies and third-party scripts. Websites need not obtain prior consent for using cookies to track users. Instead, they should provide a clear and distinct “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link on their website to allow consumers to submit an opt-out request.
Check out our complete guide on CCPA and Cookies: California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and Cookies: What you need to know
Also Read: California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) – A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
How to Obtain Consent for Using Tracking Cookies?
Websites should obtain consent from the site visitors to use tracking cookies. The best way is to use a consent management platform to manage cookie consent for your website. If you are using WordPress CMS, check out our GDPR cookie consent plugin for your consent management requirements.
GDPR Cookie consent plugin is a CMP native to WordPress, so it will work on your own server, and any consent-related data will not be shared with external servers. Using the plugin, you can completely manage cookie consent for your website.
Following are the steps you should follow to ensure cookie compliance:
- Create a cookie consent banner to disclose the use of cookies and their purpose
- Provide users with the option to accept and decline cookies
- Allow users to provide granular consent to cookies based on their categories
- Create a cookie policy and privacy policy and add the links to the cookie banner
- Allow users to withdraw and revisit the consent at any time
- Keep a record of users’ consent
- Block third-party cookies until the user gives consent
How to Block Tracking Cookies on Browsers?
As an end user, you may want to block tracking cookies from your browser. Let’s see how you can block cookies on different browsers.
Block Cookies on Google Chrome
- Click on the three vertical dots in the upper right corner near your profile icon.
- Go to the Settings menu.
- Once you are on the Chrome Settings page, go to the Privacy and security tab and select Third-party cookies.
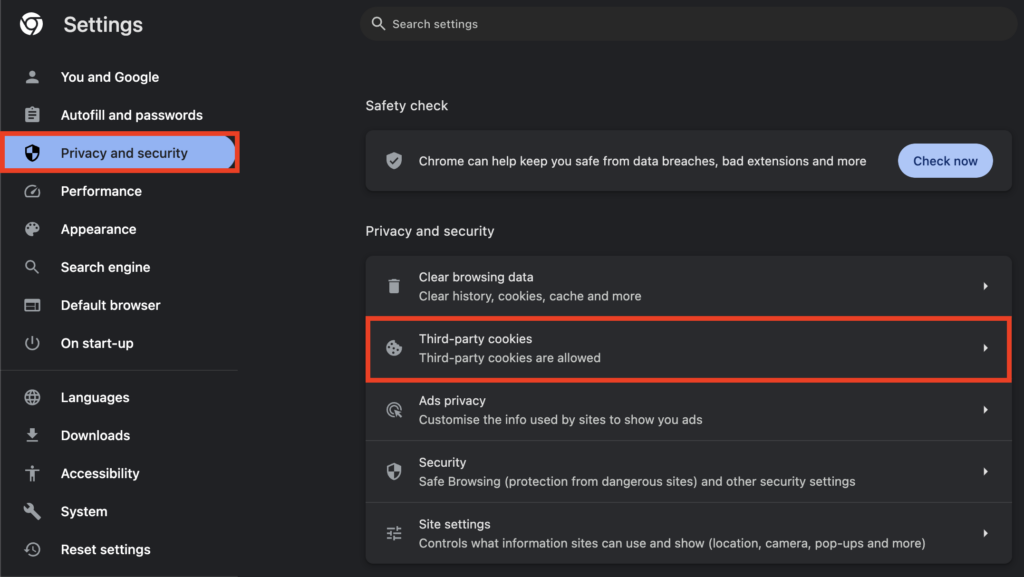
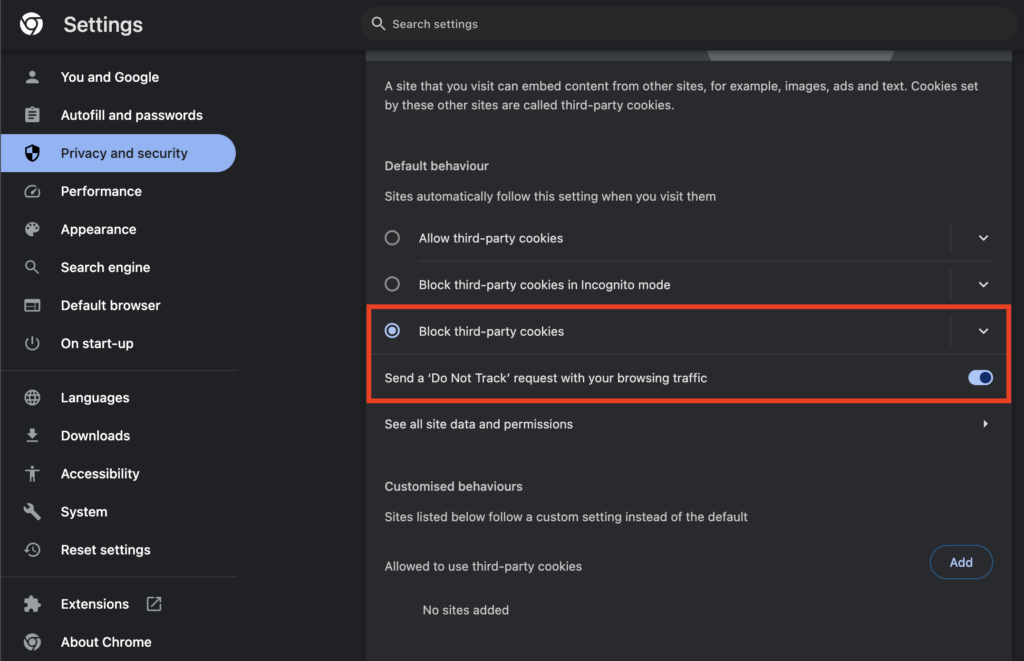
- Click on the Block third-party cookies radio button to block cookies. Additionally, you can enable the Send a ‘Do Not Track’ request with your browsing traffic checkbox.
Block Cookies on Safari
Safari, by default, blocks third-party cookies. However, you can ensure it from the following steps:
- Go to Safari > Settings from the top menu bar.
- Then click on the Advanced tab.
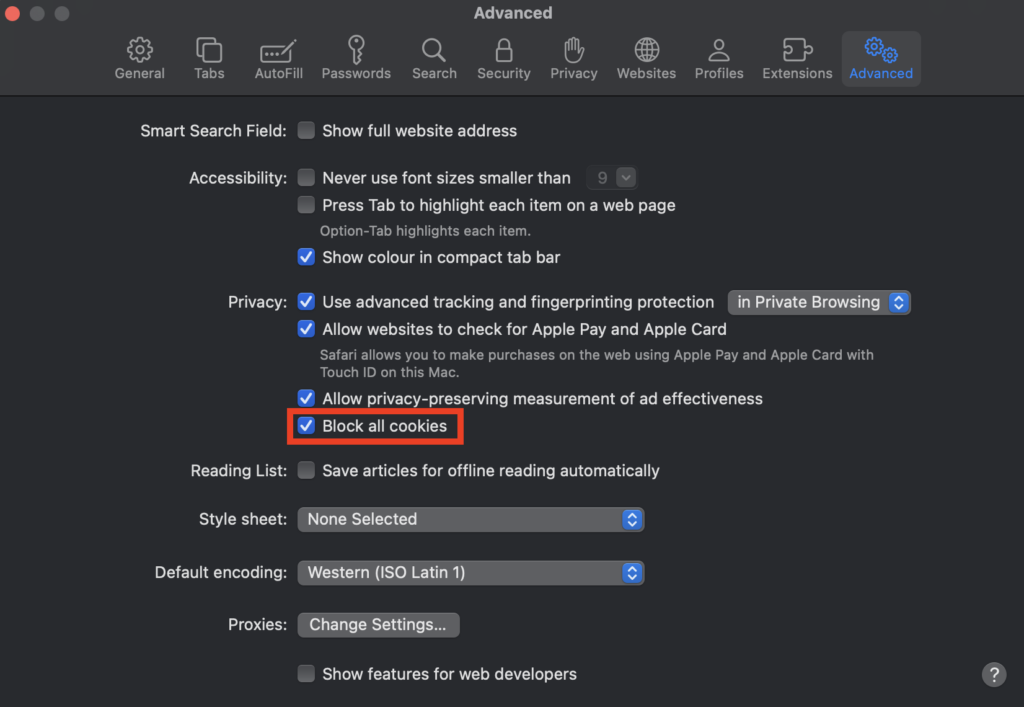
- Enable the Block all cookies checkbox.
Block Cookies on Firefox
Firefox provides users with three privacy settings options: Standard, Strict, and Custom. In all three settings, third-party cookies are automatically blocked. However, with the Custom option, you have the flexibility to select the types of cookies you want to allow.
To access these settings in Firefox:
- Click on the menu bar and go to Firefox > Preferences.
- Choose the Privacy & Security tab.
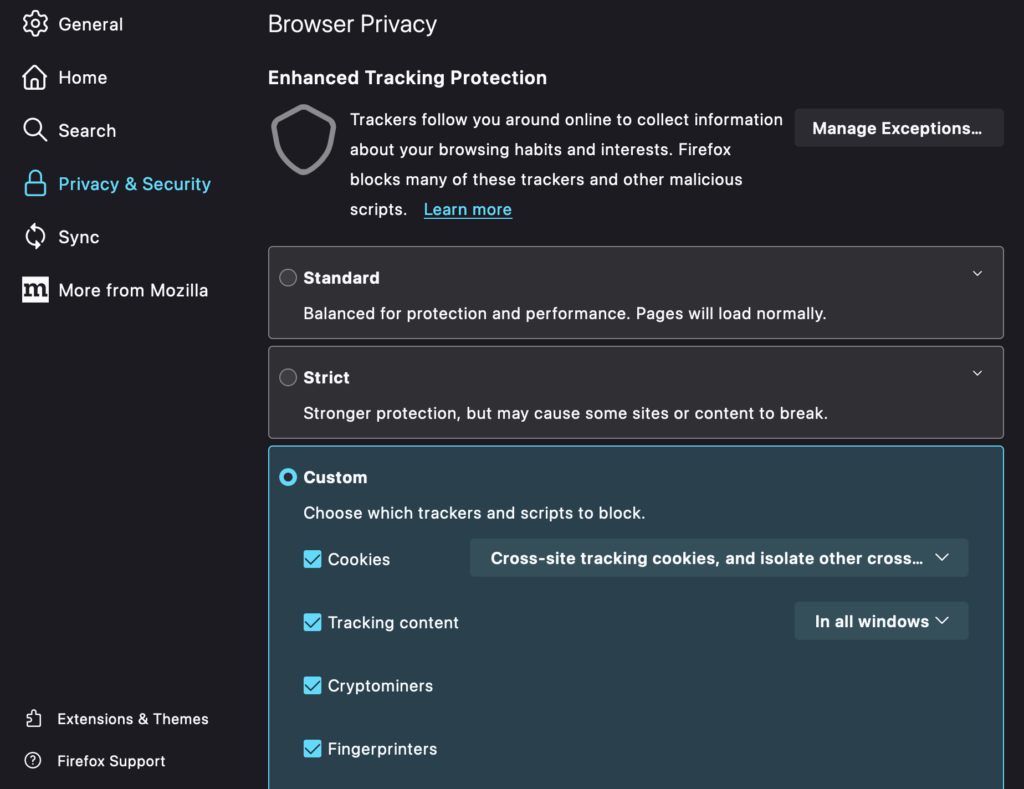
- Choose the Custom option and select the trackers or scripts you want to block.
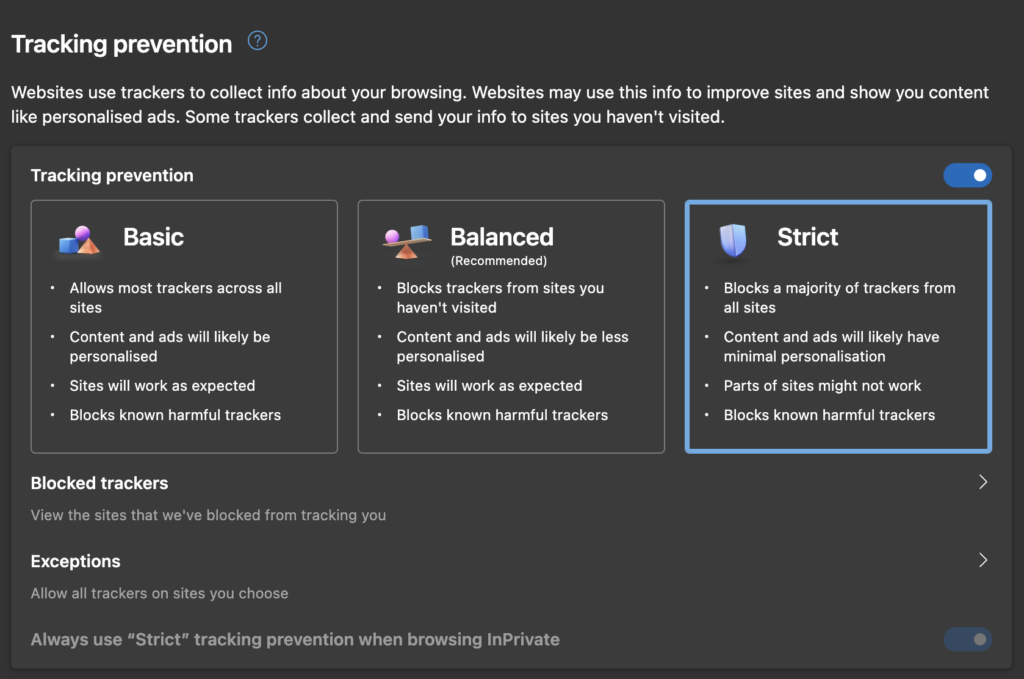
Block Cookies on Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge provides users with three levels of privacy settings: Basic, Balanced, and Strict. Strict offers the highest level of security and blocking.
To access these settings in Microsoft Edge:
- Click on the three horizontal dots next to your profile icon and choose Settings.
- Navigate to the Privacy, Search, and Services tab.
- Under Tracking Prevention settings, select Strict.
Is Google Phasing Out Tracking Cookies?
Yes. Google has officially started to phase out third-party cookies due to their privacy concerns and ability to track users across different websites. Google is aiming to implement a privacy-focused alternative to tracking cookies as part of its Privacy Sandbox initiative
As of January 4, 2024, Google has introduced a new feature called Tracking Protection, which has been rolled out to 1% of Chrome users worldwide. This feature automatically restricts third-party cookies. This initial phase serves as a testing period, allowing websites and developers to adapt in preparation for the complete removal of third-party cookies.
Google intends to fully eliminate third-party cookies for all Chrome users in Q3 of 2024, which is expected to occur between July and September.
This transition will have a substantial impact on online advertising, posing challenges for advertisers in tracking users and delivering personalized ads. Websites that heavily depend on third-party cookies for revenue or functionality will be required to adjust and explore alternative solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions on Tracking Cookies
What is a CMP?
A Consent Management Platform (CMP) is a tool that enables websites, publishers, and organizations to collect and manage user consent for processing their personal data. It helps websites to comply with data privacy laws such as GDPR and CCPA.
When a visitor lands on a website, they might see a popup or banner asking for consent to load cookies on their browsers. This popup or banner is provided by a CMP integrated into the website. Once a consent signal is received from the users, the website will be able to display ads from the vendors to the users.
Are Tracking Cookies Illegal?
As of now, tracking cookies is not illegal. However, their usage is subject to data privacy regulations and consent requirements in various jurisdictions. Websites using tracking cookies should comply with the applicable regulations and obtain consent from users. Failure to do so can result in penalties or legal action for violating users’ privacy rights.
It’s important for businesses to stay informed about the legal requirements related to tracking cookies.
What Will Replace Tracking Cookies?
Google is aiming to introduce privacy-focused alternatives to tracking cookies as part of its Privacy Sandbox initiative. While specific details about the replacement technologies are still evolving, Google’s efforts include developing new techniques for targeting ads and measuring ad effectiveness without relying on individual user tracking across different websites.
These alternatives are designed to prioritize user privacy while still enabling personalized advertising and relevant content delivery. Additionally, other industry stakeholders are also exploring alternative tracking methods, such as federated learning and cohort-based targeting, to address the evolving landscape of online advertising in a privacy-conscious manner.
Conclusion
Tracking cookies is a powerful technology that helps advertisers and marketers to track users and gain valuable insights on their websites. It also helps website visitors to view personalized content and save their preferences.
However, tracking cookies also raises some privacy concerns. Many data protection laws require websites to obtain prior consent from their visitors for using cookies.
Google is also planning to phase out tracking cookies and introduce a privacy-focused alternative that will enable websites to show personalized ads while protecting the privacy of individuals.
The emergence of these technologies signals a positive shift towards a safer digital environment.
We hope this article has helped you understand what tracking cookies are and how they will affect websites and internet users. If you have any queries, please feel free to ask them in the comments section.


